1. A rising trade deficit in India’s Balance of Payments would most likely lead to which of the following consequences?
1. Reduce foreign exchange reserves
2. Depreciation of the domestic currency
3. Decrease in the current account deficit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: Trade deficit widens 93% in Sept. as services slump
- India’s merchandise exports in September 2025 rose by ~6.74 % year-on-year to USD 36.38 billion.
- Imports for the same month increased more sharply — by ~16.6 %, reaching USD 68.53 billion.
- As a result, the trade deficit widened significantly to about USD 32.1 billion in September 2025.

Trade Deficit:
- Trade Deficit occurs when the value of a country’s imports of goods and services exceeds the value of its exports during a given period.
- Formula: Trade Deficit = Imports – Exports
Types
- Merchandise (Goods) Trade Deficit – Difference between export and import of tangible goods only.
- Current Account Deficit (CAD) – Includes goods + services + income + transfers. Trade deficit is a major component of CAD.
Causes of Trade Deficit in India
- High import dependence – especially on crude oil, gold, electronics.
- Low export diversification – concentrated in a few sectors.
- Rising global commodity prices – increases import bill.
- Strong domestic demand – boosts imports.
- Weak global demand – limits export growth.
- Currency depreciation – may not always improve exports due to import content in exports.
Implications
Positive Aspects
- Indicates strong domestic consumption and investment.
- Imports of capital goods and raw materials can boost future production capacity.
Negative Aspects
- Pressure on Current Account → widening CAD. Hence 3 is incorrect.
- Depreciation of Rupee due to higher demand for foreign currency. Hence 2 is correct.
- Inflationary pressures (imported inflation).
- May reduce foreign exchange reserves if financed unsustainably. Hence 1 is correct.
Policy Measures to Manage Trade Deficit
1. Export Promotion:
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes
- Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP)
- Make in India and India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) initiatives
2. Import Substitution:
- Encouraging domestic manufacturing (e.g., electronics, solar modules, defence).
- Atmanirbhar Bharat programs.
3. Diversification of Export Markets:
- FTAs (India–UAE CEPA, India–Australia ECTA, ongoing EU talks).
4. Macroeconomic Stability:
- Managing inflation and exchange rate through monetary/fiscal policy.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2016) Q. There has been a persistent deficit budget year after year. Which action/actions of the following can be taken by the Government to reduce the deficit? 1. Reducing revenue expenditure 2. Introducing new welfare schemes 3. Rationalizing subsidies 4. Reducing import duty Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/business/Economy/indias-exports-rise-in-september/article70166719.ece
2. With reference to the State Mining Readiness Index, consider the following statements:
I. The State Mining Readiness Index (SMRI) is a benchmarking tool introduced by the NITI Aayog.
II. Madhya Pradesh was ranked first in the State Mining Readiness Index released by the Ministry of Mines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) I only
(b) I and III
(c) II only
(d) II and III
Answer: (c) II only
Explanation:
In NEWS: Ministry of Mines releases State Mining Readiness Index and State Rankings
The State Mining Readiness Index (SMRI):
- The State Mining Readiness Index (SMRI) is a benchmarking tool introduced by the Ministry of Mines, India, to evaluate how prepared and performance‑oriented states are in the mining sector (especially for non‑coal minerals). Hence statement I is incorrect.
- It is part of the reforms framework announced in Union Budget 2025‑26, and linked to incentive schemes for states that undertake mining sector reforms.
- The SMRI is used as one component under the mining sector reforms incentive structure.
Structure, Indicators & Categories in SMRI:
The index covers multiple dimensions of state performance in the mining sector, such as:
- Auction performance – how efficiently and transparently states conduct auctions of mineral blocks.
- Early mine operationalization – the speed at which auctioned/allocated blocks are converted into functional operations (i.e. producing mines).
- Thrust on exploration – efforts by the state (or in coordination with central agencies) to explore and map mineral resources (especially non‑coal minerals).
- Sustainable mining – incorporation of environmental safeguards, closure planning, rehabilitation, implementation of “star rating” schemes, etc.
- Other supporting indicators may include regulatory environment, ease of doing mining business, institutional readiness, etc.
Categorization of states:
- States are grouped into three categories (A, B, C) based on their mineral endowment (i.e. how richly endowed they are in minerals).
- Within each category, states are ranked relative to peers with similar endowment, so that states with scarce minerals are not unfairly disadvantaged compared to states with abundant mineral resources.
Recent Rankings under SMRI & Incentive Scheme
Category A (high mineral endowment):
1. Madhya Pradesh Hence statement II is correct.
2. Rajasthan
3. Gujarat
Category B (moderate mineral endowment):
1. Goa
2. Uttar Pradesh
3. Assam
Category C (low mineral endowment):
1. Punjab
2. Uttarakhand
3. Tripura
Under the incentive scheme linked to SMRI, the top 3 states in each category are eligible for rewards (financial incentives) for achieving high performance in the index.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2019) Q. With reference to the management of minor minerals in India, consider the following statements: 1. Sand is a ‘minor mineral’ according to the prevailing law in the country. 2. State Governments have the power to grant mining leases of minor minerals, but the powers regarding the formation of rules related to the grant of minor minerals lie with the Central Government. 3. Stale Governments have the power to frame rules to prevent illegal mining of minor minerals. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 3 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2179742
3. Which among the following is the Indo-Indonesian Joint Bilateral Maritime Exercise, recently seen in the news?
(a) Samudra Shakti
(b) Konkan
(c) Mitra Shakti
(d) Indra
Answer: (a) Samudra Shakti
Explanation:
In NEWS: The Indian Navy is hosting the fifth edition of the Indo-Indonesian Joint Bilateral Maritime Exercise, ‘Samudra Shakti – 2025’
‘Samudra Shakti – 2025’:
- Samudra Shakti – 2025 is a bilateral naval exercise between the Indian Navy and the Indonesian Navy, conducted off the coast of Visakhapatnam. Hence option (a) is correct.
- The Indian Navy was represented by INS Kavaratti, an anti-submarine warfare corvette, while the Indonesian Navy deployed KRI John Lie, a corvette equipped with a helicopter.
- The exercise was conducted in two phases – a harbour phase and a sea phase.
- During the harbour phase, both navies engaged in cross-deck visits, joint yoga sessions, sports events, and expert-level exchanges.
- In the sea phase, the navies undertook complex maritime operations including air defence drills, helicopter operations, weapon firing, and Visit, Board, Search, and Seizure (VBSS) exercises.
- The primary objective of Samudra Shakti – 2025 is to enhance interoperability, maritime cooperation, and mutual understanding between India and Indonesia in the Indo-Pacific region.
- This exercise reflects the growing strategic partnership between the two nations and supports their shared commitment to maintaining security and stability in regional waters.
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2179326
4. Which country has been recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO) as the first in the world to achieve the triple elimination of mother-to-child transmission of HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis B?
(a) Sri Lanka
(b) Maldives
(c) Bhutan
(d) India
Answer: (b) Maldives
Explanation:
In NEWS: What India can learn from Maldives’ parent-to-child triple elimination of diseases
Lessons from Maldives:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has validated the Maldives for eliminating mother-to-child transmission (EMTCT) of hepatitis B, adding to its earlier validation for EMTCT of HIV and syphilis in 2019.
- This makes Maldives the first country in the world to achieve triple elimination of mother-to-child transmission of HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis B. Hence option (b) is correct.
- The achievement is credited to strong political will, sustained investment in maternal and child health, and universal health coverage guaranteeing free antenatal care, vaccines, and diagnostics for all residents, including migrants.
- Over 95% of pregnant women in Maldives receive antenatal care and are tested for HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis B. Newborns receive timely hepatitis B birth doses and full vaccine coverage.
- As a result, no babies were born with HIV or syphilis in 2022 and 2023, and a 2023 national survey found zero hepatitis B infections among young children.
- Maldives invests over 10% of its GDP in health, and the success reflects strong partnerships across government, private sector, civil society, and international organizations like WHO.
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus):
A virus that attacks the body’s immune system, specifically the CD4 cells (T cells), making it harder for the body to fight infections and diseases. If untreated, HIV can lead to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
Syphilis:
A sexually transmitted bacterial infection caused by Treponema pallidum. It progresses in stages and can cause serious health problems if left untreated, including damage to the heart, brain, and other organs.
Hepatitis B:
A viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic liver disease. It spreads through contact with infected bodily fluids, such as blood or sexual contact, and can lead to liver cirrhosis or cancer if untreated.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2014) Q. Consider the following diseases 1. Diphtheria 2. Chickenpox 3. Smallpox Which of the above diseases has/have been eradicated in India? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 1, 2 and 3 (d) None |
5. With respect to the elections to the UN Human Rights Council, consider the following statements:
I. Members once elected are not eligible for re-election.
II. Members are elected by the UN General Assembly.
III. A member state must secure an absolute majority of votes to be elected.
IV. The membership is for a three-year term.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) II and IV only
(b) I, II and III
(c) II, III and IV
(d) I and III only
Answer: (c) II, III and IV
Explanation:
In NEWS: India Elected Unopposed to UN Human Rights Council for 2026–28 Term
- This marks India’s fourth consecutive term as a member of the 47-member council, which is responsible for promoting and protecting human rights globally.
UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC):
- The UNHRC is an intergovernmental body within the United Nations responsible for promoting and protecting human rights worldwide.
- It has 47 member states, elected by the UN General Assembly.
How are members elected?
- Members are elected by the UN General Assembly for three-year terms. Hence statements II and IV are correct.
Seats are distributed based on regional groups to ensure geographic representation:
- African States
- Asia-Pacific States
- Eastern European States
- Latin American and Caribbean States
- Western European and Other States
- A member state must secure an absolute majority of votes in the General Assembly to be elected. Hence statement III is correct.
- Members are generally eligible for two consecutive terms, after which they must step down for at least one term before seeking re-election. Hence statement I is incorrect.
- Countries often campaign for seats years in advance.
- Sometimes, countries are elected unopposed if the number of candidates equals the number of available seats in their regional group.
- Once elected, member states participate in sessions, report on human rights situations, and vote on resolutions.
Functions of UNHRC:
- Promote and protect human rights globally.
- Investigate and respond to human rights violations.
- Conduct Universal Periodic Reviews (UPR) of all UN member states.
- Issue resolutions and recommendations on human rights.
- Support special rapporteurs and expert groups on human rights issues.
- Facilitate international cooperation on human rights.
- Hold special sessions for urgent human rights crises.
- Promote implementation of international human rights treaties.
| PYQ REFERENCE: Q. Other than the Fundamental Rights, which of the following parts of the Constitution of India reflect/reflects the principles and provisions of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948)? (2020) 1. Preamble 2. Directive Principles of State Policy 3. Fundamental Duties Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Q. Consider the following: 1. Right to education. 2. Right to equal access to public service. 3. Right to food. Which of the above is/are Human Right/Human Rights under “Universal Declaration of Human Rights”? (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Source: https://www.newsonair.gov.in/india-elected-unopposed-to-un-human-rights-council-for-2026-28-term/
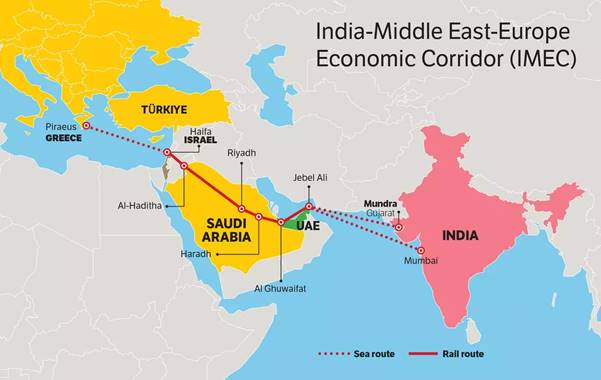
6. With reference to ‘India-Middle East-Europe Corridor Project’ consider the following statements.
1. The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) is a planned economic corridor that aims to bolster economic development by fostering connectivity and economic integration between Asia, the Persian Gulf and Europe.
2.The project was launched to bolster transportation and communication links through rail and shipping networks and also to counter China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
3. The corridor is a proposed route from India to Europe through the Suez Canal.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: The India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor visualises maritime connectivity between India and the Arabian Peninsula, as well as high-speed trains running from the ports in the UAE to the Haifa port through Saudi Arabia and Jordan. However, the situation in West Asia mandates that the corridor’s routes adapt to political dynamics
The India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor:
- The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) is a planned economic corridor that aims to bolster economic development by fostering connectivity and economic integration between Asia, the Persian Gulf and Europe. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The corridor is a proposed route from India to Europe through the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Israel and Greece. Hence statement 3 is incorrect.
- On 09 September 2023 the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed during the 2023 G20 New Delhi summit by the governments of India, United States, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, France, Germany, Italy and the European Union.
- The project was launched to bolster transportation and communication links between Europe and Asia through rail and shipping networks and is seen as a counter to China’s Belt and Road Initiative. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- The memorandum of understanding document has only mapped out the potential geography of a corridor and will compete against the current trade route going through the Suez Canal.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2024) Q. Consider the following statements: Statement-I: Sumed pipeline is a strategic route for Persian Gulf oil and natural gas shipment to Europe Statement-II: Sumed pipeline connects the Red Sea with the Mediterranean Sea. Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements? (a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I (b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I (c) Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect (d) Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct |
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/the-future-of-the-imec/article70168507.ece
7. Consider the following statements with respect to the World Trade Organization (WTO):
1. The World Trade Organization (WTO) is the only global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations.
2. India is one of the founding members of the World Trade Organization (WTO), which came into force on 1 January 1995.
3. It follows the Most Favoured Nation (MFN) principles by discriminating between its trading partners.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
(a) 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer: (b) 3 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: China files WTO complaint on India’s EV, battery subsidies
WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION (WTO)
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) is the only global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It ensures that trade flows smoothly, predictably, and freely as possible among member countries.
- Came into existence: 1 January 1995
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- Replaced: General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), established in 1947
- Current Membership: 164 members (as of 2025)
- India: Founding member. Hence statement 2 is correct
Objectives
- Promote free and fair international trade.
- Ensure non-discrimination (Most-Favoured-Nation & National Treatment principles).
- Encourage predictability and transparency in trade policies.
- Promote economic development, especially in developing countries.
- Settle trade disputes through a structured mechanism.
Key Principles
| Principle | Meaning |
| Most Favoured Nation (MFN) | A country cannot discriminate between its trading partners. Hence statement 3 is incorrect. |
| National Treatment | Imported and locally produced goods should be treated equally once they enter the market. |
| Transparency | Members must publish trade regulations and notify changes. |
| Reciprocity | Mutual reduction of trade barriers. |
| Special and Differential Treatment (SDT) | Flexibilities for developing and least-developed countries. |
Structure
- Ministerial Conference – highest decision-making body; meets biennially.
- General Council – conducts day-to-day work, also meets as Dispute Settlement Body (DSB) and Trade Policy Review Body (TPRB).
- Committees and Councils – e.g., Council for Goods, Services, TRIPS, etc.
- Director-General – administrative head. (As of 2025: Dr. Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala)
Major Agreements under WTO
| Agreement | Purpose |
| GATT (Goods) | Trade in goods, tariff reduction. |
| GATS (Services) | Trade in services like banking, telecom, etc. |
| TRIPS | Intellectual property rights. |
| TRIMS | Investment measures related to trade. |
| AoA (Agreement on Agriculture) | Fair competition and reduction of subsidies. |
| SPS (Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures) | Food safety and animal/plant health. |
| TBT (Technical Barriers to Trade) | Standards and regulations in trade. |
Dispute Settlement Mechanism (DSM)
- Core function: ensures rules-based trade.
- If members violate rules, disputes are handled through consultation, panel, appeal, and implementation.
- Appellate Body crisis since 2019 — U.S. blocking appointments → dispute settlement stalled.
India’s Interests:
- Protecting farmers from unfair subsidies by developed nations.
- Promoting services exports (IT, health, education).
- Ensuring patent flexibility under TRIPS for affordable medicines.
- Safeguarding food security via Public Stockholding (PSH).
Key Issues for India:
- Agricultural subsidies by rich countries distort trade.
- E-commerce & digital trade regulation concerns.
- Fishery subsidy negotiations – India demands special treatment for artisanal fishers.
- Trade and climate change linkages.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2017) Q. Consider the following statements: 1. India has ratified the Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) of WTO. 2. TFA is a part of WTO’s Bali Ministerial Package of 2013. 3. TFA came into force in January 2016. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 1 and 3 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
8. The Rafah Border Crossing, recently in news, connects which of the following regions?
(a) Israel and Lebanon
(b) Gaza Strip and Egypt
(c) West Bank and Jordan
(d) Syria and Turkey
Answer: (b) Gaza Strip and Egypt
Explanation:
In NEWS: Aid enters Gaza, Israel to open Rafah crossing
Rafah crossing:
- The Rafah Border Crossing is the sole crossing point between the Gaza Strip and Egypt. Hence option (b) is correct.
- Situated at the southern tip of Gaza, it connects Rafah city in Gaza with North Sinai in Egypt.
- It is not connected to Israel—unlike other Gaza border crossings.
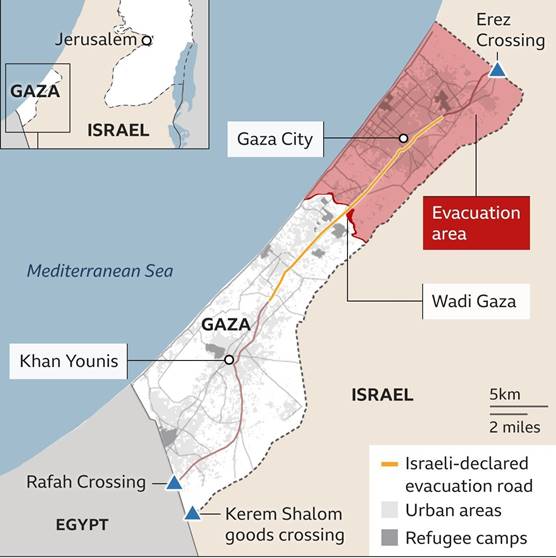
Strategic Importance
- It is Gaza’s only gateway to the outside world that is not controlled by Israel.
- Acts as the primary route for humanitarian aid, medical evacuation, and people’s movement in and out of Gaza.
- Egypt controls entry and exit; Israel has no direct control, but it coordinates with Egypt on security aspects.
Political & Security Context
- Since Hamas took control of Gaza in 2007, Israel and Egypt have imposed tight border restrictions citing security threats.
- The Rafah crossing is often opened temporarily for humanitarian reasons or under international mediation.
- It frequently becomes a flashpoint during conflicts, especially when humanitarian aid or refugees try to pass through.
- Managed by Egyptian authorities in coordination with the Palestinian Authority (PA) and sometimes Hamas (de facto in Gaza).
Recent Developments (2023–2025)
- During the Israel–Hamas conflict (2023–25), Rafah crossing became the key entry point for humanitarian aid from Egypt to Gaza, especially from the city of El-Arish.
- Aid convoys, ambulances, and fuel trucks have passed through under UN and Egyptian supervision.
- Israel’s military operations near Rafah (2024–25) raised concerns about civilian casualties and potential refugee outflow into Egypt.
- Egypt has maintained a controlled humanitarian access, refusing large-scale refugee entry to protect its Sinai security and sovereignty concerns.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2008) Q. Yom Kippur War was fought between which sides/ countries? (a) Turkey and Greece (b) Serbs and Croats (c) Israel, and Arab countries led by Egypt and Syria (d) Iran and Iraq |
9. The Campi Flegrei volcano, seen in the news recently, is located in which one of the following countries?
(a) Japan
(b) Greece
(c) Italy
(d) Argentina
Answer: (c) Italy
Explanation:
In NEWS: AI reveals hidden ‘ring fault’ that is unleashing earthquakes at Italy’s Campi Flegrei volcano
- A new AI‑based approach has revealed a “ring fault” structure beneath the Campi Flegrei volcano.
- Between 2022 and 2025, more than 54,000 earthquakes were mapped using this AI method.
Campi Flegrei volcano:
- Campi Flegrei is a large volcanic caldera located west of Naples, Italy. Hence option (c) is correct.
- Its name means “Burning Fields” in Italian, referencing the area’s frequent geothermal activity.
- It is one of the most dangerous supervolcanoes in the world due to its size, explosive history, and proximity to a densely populated region.
- The caldera last erupted in 1538, forming a small cone called Monte Nuovo.
- Campi Flegrei has experienced periodic unrest, including ground uplift, gas emissions, and swarms of earthquakes.
- This phenomenon, known as bradyseism, involves slow, vertical ground movement due to changes in pressure underground.
- In recent years, the area has seen a significant increase in seismic activity and ground deformation.
- A new AI-based study has discovered a hidden ring fault beneath the volcano that may explain the current earthquake patterns.
- The presence of this fault suggests localized stress release, but there is no clear evidence of magma rising toward the surface.
- Although there is no imminent eruption, scientists are closely monitoring the area to assess potential volcanic and seismic hazards.
10. With reference to Indian elephants, consider the following statements:
1. The leader of an elephant group is a female.
2. The maximum gestation period can be 22 months.
3. An elephant can normally go on calving till the age of 40 years only.
4. Among the States in India, the highest elephant population is in Kerala.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- Elephant herds are matriarchal. The leader is usually the oldest and most experienced female, called the matriarch.
- Elephants have the longest gestation period among land mammals, up to 22 months. This applies to Indian (Asian) elephants as well.
- Female elephants can reproduce until around 50–60 years of age, although fertility may decline with age.
- As per the latest estimates, Karnataka has the highest elephant population in India, followed by Assam and Kerala.
Hence option (a) is correct.

