1. Consider the following statements regarding the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD):
1. It is an international legally binding treaty adopted at the Rio Earth Summit in 1992.
2. It recognizes biological resources over national sovereignty as the common heritage of mankind.
3. India is a party to the convention since 1994.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: Panama meeting: Parties fail to agree on text of recommendations for Conventional on Biological Diversity
Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD):
- The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) is an international legally binding treaty adopted at the Rio Earth Summit in 1992 (entered into force in 1993). Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Secretariat: Based in Montreal, Canada.
- India is a party to the convention since 1994. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Objectives of the CBD
- Conservation of biological diversity.
- Sustainable use of its components.
- Fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the use of genetic resources (Access and Benefit Sharing – ABS).
Key Features
- Recognizes national sovereignty over biological resources (not a global commons). Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
- Promotes in-situ (protected areas, biosphere reserves) and ex-situ (seed banks, gene banks) conservation.
- Encourages traditional knowledge protection and indigenous community participation.
- The Cartagena Protocol (2000) deals with biosafety and LMOs (Living Modified Organisms).
- The Nagoya Protocol (2010) focuses on Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) mechanisms.
- The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) (adopted in 2022) replaced the Aichi Targets (2010–2020), setting new global goals for 2030.
India’s Implementation
- Enacted the Biological Diversity Act, 2002.
- Established the National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) at Chennai.
- Prepared National Biodiversity Action Plan (NBAP) and People’s Biodiversity Registers (PBRs).
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2014) Q. With reference to ‘Global Environment Facility’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (a) It serves as financial mechanism for ‘Convention on Biological Diversity’ and ‘United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change’ (b) It undertakes scientific research on environmental issues at global level (c) It is an agency under OECD to facilitate the transfer of technology and funds to underdeveloped countries with specific aim to protect their environment (d) Both (a) and (b) |
2. Consider the following pairs:
| S.no | Scheme | Ministry | Objective |
| 1. | Atal Pension Yojana (APY) | Ministry of Finance | To provide a guaranteed pension ensuring old-age income security for unorganised sector workers. |
| 2. | Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY) | Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment | To provide free assisted-living devices to BPL senior citizens with age-related disabilities. |
| 3. | SAGE Portal | Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment | To promote start-ups providing innovative products and services for the elderly (“Silver Economy”). |
| 4. | SACRED Portal | Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment | To connect senior citizens (60+) with employment opportunities for dignified re-engagement. |
How many of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All the four
Answer: (d) All the four
Explanation:
In NEWS: Elderly in India – Population, Challenges, and Government Initiatives
Demographic Profile:
- India’s elderly population (60+) is projected to increase from 100 million (2011) to 230 million (2036) — about 15% of the population.
- By 2050 → expected to reach 319 million (LASI Report 2021).
- Sex ratio (elderly): 1,065 females per 1,000 males; 58% are women, 54% of whom are widows.
- Dependency ratio: 62 dependents per 100 working-age individuals.
- Regional variation:
- Kerala → 13% (2011) → 23% (2036)
- Uttar Pradesh → 7% (2011) → 12% (2036)
- Southern States + Himachal Pradesh + Punjab = highest elderly share
Challenges Faced by Elderly
The elderly in India often find themselves in vulnerable positions due to a lack of adequate support systems, both institutional and familial. They confront multifaceted challenges including:
- Health: Stigmatised mental health conditions (dementia, Alzheimer’s), rising disabilities, inadequate geriatric infrastructure, Urban-rural divide in access to medical services.
- Economic Insufficient social security provisions, rise of living and medical expenses, limited financial resources.
- Social: Weakening family support systems, social isolation, neglect, lack of companionship etc.
- Digital divide: Technology adoption barriers, lack of training and accessible devices.
- Infrastructure: Inadequate literacy, emergency response system overlooking elderly as vulnerable group. Public spaces and transport in India is largely not elderly-friendly since ramps, handrails and accessible washrooms are missing in many areas.
Government Schemes for Senior Citizens – Ministry & Objective
| Scheme | Ministry | Objective |
| Atal Pension Yojana (APY) | Ministry of Finance / PFRDA | To provide a guaranteed pension (₹1,000–₹5,000) ensuring old-age income security for unorganised sector workers. |
| Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY) | Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment (MoSJE) | Umbrella scheme for empowerment, inclusion, and well-being of senior citizens. |
| Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC) | MoSJE | To provide shelter, food, and healthcare facilities to indigent senior citizens through grants-in-aid. |
| Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY) | MoSJE / ALIMCO | To provide free assisted-living devices to BPL senior citizens with age-related disabilities. |
| Elderline (Helpline 14567) | MoSJE | To provide a 24×7 national helpline for grievance redressal and emotional support to senior citizens. |
| SAGE Portal (Senior Care Ageing Growth Engine) | MoSJE / IFCI | To promote start-ups providing innovative products and services for the elderly (“Silver Economy”). |
| SACRED Portal | MoSJE | To connect senior citizens (60+) with employment opportunities for dignified re-engagement. |
| Geriatric Caregiver Training | MoSJE / NISD | To train caregivers for professional elderly care and support services. |
| Ayushman Bharat – PMJAY (Elderly Expansion) | Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW) | To provide ₹5 lakh annual health insurance coverage for senior citizens aged 70+. |
| IGNOAPS (under NSAP) | Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) | To provide non-contributory old-age pension to BPL senior citizens (60+). |
| National Programme for Health Care of the Elderly (NPHCE) | MoHFW | To provide accessible and comprehensive healthcare services for elderly persons. |
| Senior Citizens’ Welfare Fund (SCWF) | MoSJE | To use unclaimed deposits for financing various welfare schemes for senior citizens. |
Hence all the pairs are correct.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2016) Q. Regarding ‘Atal Pension Yojana’, which of the following statements is/are correct? 1. It is a minimum guaranteed pension scheme mainly targeted at unorganized sector workers. 2. Only one member of a family can join the scheme. 3. Same amount of pension is guaranteed for the spouse for life after subscriber’s death. Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2183196
3. Which among the following statements is/are correct with respect to the ‘Nutrient Based Subsidy Scheme’?
1. It was launched by the Department of Fertilizers, under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare.
2. The scheme covers Phosphatic and Potassic (P&K) fertilizers including Urea.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (d) Neither 1 nor 2
Explanation:
In NEWS: Cabinet approves the Nutrient Based Subsidy rates for Rabi 2025- 26 on Phosphatic and Potassic fertilizers
Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) Scheme:
- The Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) Scheme was launched in April 2010 by the Department of Fertilizers, under the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- The scheme covers Phosphatic and Potassic (P&K) fertilizers, excluding Urea (which remains under a separate controlled subsidy). Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
- Under NBS, the subsidy is fixed per kilogram of nutrient content — Nitrogen (N), Phosphate (P), Potash (K), and Sulphur (S).
- The subsidy is provided directly to fertilizer companies, who sell fertilizers to farmers at subsidized rates.
- The scheme aims to encourage balanced fertilization, promoting judicious use of all nutrients rather than overuse of urea (Nitrogen).
- It also enables farmers to access fertilizers at affordable prices and supports soil health management.
- The rates of subsidy per nutrient are notified annually by the Government based on global prices and domestic needs.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2017) Q. Consider the following statements: The nation-wide ‘Soil Health Card Scheme’ aims at 1. expanding the cultivable area under irrigation. 2. enabling the banks to assess the quantum of loans to be granted to farmers on the basis of soil quality. 3. checking the overuse of fertilizers in farmlands. Which of the above statements is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2183291
4. Consider the following countries:
1. India
2.Indonesia
3. Malaysia
4. Myanmar
5. China
Which of the above are members of the International Pepper Community?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 4
(c) 2 and 5
(d) 3, 4 and 5
Answer: (a) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
In NEWS: Global Pepper Industry Convenes in Kochi for the 53rd International Pepper Community Annual Sessions
International Pepper Community (IPC):
- The International Pepper Community (IPC) is an intergovernmental organization of pepper-producing countries, established under the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UN-ESCAP).
- It was set up in 1972, with headquarters in Jakarta, Indonesia.
- The IPC promotes the production, trade, and research related to pepper (Piper nigrum) and other spices.
- India is a founding and active member of the IPC.
- The Spices Board of India (under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry) represents India in the IPC.
- India hosted several IPC Sessions and Spice Conferences, promoting sustainable pepper farming.
Member Countries
- Founding members: India, Indonesia, and Malaysia.
- Other members: Sri Lanka, Vietnam, Brazil, and Papua New Guinea.
- Associate members and observers: Various spice-producing and importing countries. Hence option (a) 1, 2 and 3 are correct.
Objectives
- Promote international cooperation in pepper production and trade.
- Facilitate research and development to improve yield and quality.
- Collect, analyse, and disseminate market and price information.
- Encourage value addition and fair trade practices.
- Provide a forum for policy coordination among member countries.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2022) Q. Consider the following countries: 1. Armenia 2. Azerbaijan 3. Croatia 4. Romania 5. Uzbekistan Which of the above are members of the Organization of Turkic States? (a) 1, 2 and 4 (b) 1 and 3 (c) 2 and 5 (d) 3, 4 and 5 |
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2183513
5. With reference to the International Solar Alliance (ISA), consider the following statements:
1. The International Solar Alliance (ISA) was jointly launched by India and France during the COP 21 (Paris Climate Conference).
2. Membership of ISA was limited to countries lying between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
3. India spearheaded the “One Sun, One World, One Grid (OSOWOG)” initiative to create a global solar power grid.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (c) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: The President of India, inaugurated the opening plenary of the Eighth Session of the International Solar Alliance Assembly (ISA) in New Delhi
International Solar Alliance (ISA):
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) was jointly launched by India and France on 30th November 2015 during the COP 21 (Paris Climate Conference). Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The ISA Headquarters is located in Gurugram, Haryana, making it the first treaty-based intergovernmental organization headquartered in India.
- The Framework Agreement of ISA came into force on 6th December 2017.
- Membership of ISA was initially limited to countries lying between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, but is now open to all UN member states. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
- As of 2025, ISA has 116 signatory countries and 90 countries have ratified its Framework Agreement.
Objective:
- The main objective of ISA is to mobilize USD 1 trillion in solar investments by 2030 to promote global solar deployment.
- ISA works to reduce the cost of solar energy, mobilize finance, share technology, and build capacity among member countries.
- The Alliance promotes the concept of energy access, equity, and sustainability, especially for Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and Small Island Developing States (SIDS).
- The ISA’s vision is reflected in its “Towards 1000” strategy (2023–2030) aiming for:
- 1000 GW of solar capacity,
- USD 1000 billion mobilized, and
- 1000 million people benefitted.
Major ISA initiatives include:
- STAR-C (Solar Technology and Application Resource Centre) for capacity building.
- Global Solar Atlas for resource mapping.
- Solar Financing Facility for de-risking investments.
- Solar Mini-Grids and Solar Cold Chain Projects for rural and agricultural applications
India’s Role:
- The 8th Assembly of ISA (2025) was held in New Delhi, inaugurated by the President of India, under the theme “Solar Energy – Empowering Lives, Enabling Development.”
- India serves as the host country and depository of the ISA Framework Agreement.
- The ISA promotes the “One Sun, One World, One Grid (OSOWOG)” initiative, spearheaded by India, to create a global solar power grid. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- India’s leadership in ISA demonstrates its commitment to climate diplomacy and South-South cooperation.
- ISA’s initiatives are part of India’s broader efforts to become a renewable energy hub and achieve net-zero emissions by 2070.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2025) Q. Consider the following statements about PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana: I. It targets installation of one crore solar rooftop panels in the residential sector. II. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy aims to impart training on installation, operation, maintenance and repairs of solar rooftop systems at grassroot levels. III. It aims to create more than three lakhs skilled manpower through fresh skilling, and upskilling, under scheme component of capacity building. Which of the statements given above are correct? (a) I and II only (b) I and III only (c) II and III only (d) I, II and III |
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2183262
6. Consider the following statements:
1. Cloud seeding is a type of weather modification that aims to change the amount or type of precipitation, mitigate hail, or disperse fog.
2. Silver iodide and potassium iodide are the most commonly used agents to promote nucleation and precipitation.
3. Cloud seeding is relatively inexpensive Compared to other water augmentation strategies
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Answer: (c) All three
Explanation:
In NEWS: Cloud-seeding trials done in Delhi to combat air pollution
Cloud seeding:
- Cloud seeding is the process of adding special substances like silver iodide and dry ice to clouds to make it rain or snow in areas experiencing water scarcity, less snowfall, or to reduce hail and clear fog. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It can be done using airplanes, rockets, or machines on the ground.
- Common agents including silver iodide, potassium iodide, dry ice, urea, and table salt, but pollen, bacteria (especially Pseudomonas), and dust also have surfaces that promote nucleation and precipitation. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- These materials encourage cloud droplets to form and fall as rain or snow.
- The process requires existing clouds and can increase rainfall by 5-15 per cent.
- It is used to address water scarcity, reduce hail, or clear fog.
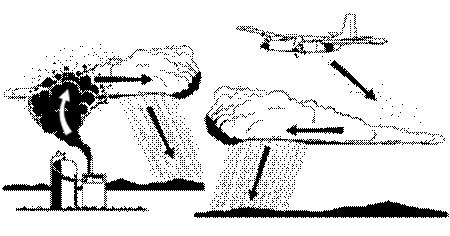
Pros
- Enhances Rainfall or Snowfall: It potentially increases precipitation. This benefits agriculture and water reservoirs and might mitigate the impact of damaging weather.
- Cost-effective: Compared to other water augmentation strategies, cloud seeding is relatively inexpensive. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Cons
- Uncertain Outcomes: The effectiveness of cloud seeding is variable and dependent on atmospheric conditions.
- Environmental Concerns: There are concerns about the potential toxicity of the chemicals. For example, excessive sodium degrades soil and affects plant growth, while silver is toxic to aquatic life.
- Weather Interference: Manipulating weather patterns in one area inadvertently affects weather elsewhere.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2025) Q. Artificial way of causing rainfall to reduce air pollution makes use of (a) silver iodide and potassium iodide (b) silver nitrate and potassium iodide (c) silver iodide and potassium nitrate (d) silver nitrate and potassium chloride |
7. Consider the following statements:
Statement I: Exposure to fine particulate matter (PM₂.₅) is more harmful to human health than exposure to coarse particulate matter (PM₁₀).
Statement II: PM₁₀ particles are can penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream.
Statement III: PM₂.₅ particles, due to their smaller size, remain suspended longer and can travel long distances.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement II and Statement III are correct and both of them explain Statement I
(b) Both Statement II and Statement III are correct but only one of them explains Statement I
(c) Only one of the Statements II and III is correct and that explains Statement I
(d) Neither Statement II nor Statement III is correct
Answer: (c) Only one of the Statements II and III is correct and that explains Statement I
Explanation:
In NEWS: PM 2.5 not only killed 1.7 million people in India during 2022, but also caused financial losses to the tune of 9.5% of country’s GDP: Lancet
Particulate Matter (PM):
1. Particulate Matter (PM) refers to a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets suspended in the air.
2. PM includes dust, dirt, soot, smoke, and liquid droplets, originating from both natural and anthropogenic sources.
3. PM is classified mainly into two categories based on size:
- PM₁₀ – particles with diameter ≤10 micrometres (µm).
- PM₂.₅ – fine particles with diameter ≤2.5 micrometres (µm).
- PM₂.₅ – Remains suspended longer; can travel long distances. Hence statement III is correct.
- PM₁₀ – Settles faster due to larger size
4. PM₂.₅ particles are more hazardous as they can penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream. Hence statement II is incorrect.
5. Major sources of PM include vehicular emissions, industrial activities, construction dust, biomass burning, thermal power plants, and crop residue burning.
6. Secondary particulate matter forms in the atmosphere from chemical reactions involving gases such as SO₂, NOx, NH₃, and VOCs.
7. PM pollution is a key component of urban smog and significantly reduces visibility and air quality.
8. PM₂.₅ is the most harmful air pollutant linked to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and premature deaths.
9. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) 2021 Air Quality Guidelines:
- Annual mean limit for PM₂.₅ is 5 µg/m³.
- Annual mean limit for PM₁₀ is 15 µg/m³.
10. As per India’s National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) (CPCB, 2009):
- PM₂.₅: 40 µg/m³ (annual average)
- PM₁₀: 60 µg/m³ (annual average).
11. Delhi, Kanpur, Lucknow, and Patna are among the cities with the highest PM₂.₅ concentrations in India.
12. PM is monitored under the National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP) and Continuous Ambient Air Quality Monitoring Stations (CAAQMS).
13. The Air Quality Index (AQI) in India measures air pollutants including PM₁₀ and PM₂.₅, along with NO₂, SO₂, CO, O₃, NH₃, and Pb.
14. High PM concentration leads to acid rain, haze formation, and climate forcing due to absorption and scattering of sunlight.
15. The National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) (launched in 2019) aims to reduce PM₂.₅ and PM₁₀ levels by 40% by 2026 (from 2017 levels).
16. Odd–Even scheme, smog towers, and anti-smog guns are short-term interventions to control PM pollution in urban areas.
17. Biofuel promotion, electric mobility, crop residue management, and clean cooking fuel (Ujjwala Yojana) help reduce PM emissions.
18. PM also contributes to black carbon formation, which accelerates glacial melting in the Himalayas.
19. Vehicular emissions, especially from diesel engines, are a major source of PM₂.₅ and black carbon in Indian cities.
20. Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) regulate PM levels under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2022) Q. In the context of WHO Air Quality Guidelines, consider the following statements: 1. The 24-hour mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 15 µg/m³ and annual mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 5 µg/m3. 2. In a year, the highest levels of ozone pollution occur during the periods of inclement weather. 3. PM10 can penetrate the lung barrier and enter the bloodstream. 4. Excessive ozone in the air can trigger asthma. Which of the statements given above are correct? (a) 1, 3 and 4 (b) 1 and 4 only (c) 2, 3 and 4 (d) 1 and 2 only |
8. Consider the following statements regarding Mount Fuji:
1. It is a stratovolcano that lies at the junction of three tectonic plates, the Amurian Plate, Okhotsk Plate, and Philippine Sea Plate.
2. It is a symbol of Japan and a UNESCO World Heritage Site (2013) under the category “Cultural Site.”
3. Mount Fuji is classified as an active volcano because of its frequent eruptions in the last decade.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Answer: (b) Only two
Explanation:
In NEWS: The peak of Japan’s Mount Fuji was capped with snow for the first time this winter on October 23, reaching the milestone 21 days later than the average since records began in 1894, the country’s meteorological agency said.


Mount Fuji:
- Mount Fuji (Fujisan) is an active stratovolcano located on Honshu Island, Japan.
- It is situated about 100 km southwest of Tokyo and is Japan’s highest peak at 3,776 metres (12,389 ft).
- Mount Fuji lies at the junction of three tectonic plates — the Amurian Plate, Okhotsk Plate, and Philippine Sea Plate. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- It is classified as a composite volcano, formed by alternating layers of lava flows, volcanic ash, and rocks.
- The mountain has erupted several times; the last recorded eruption occurred in 1707 (Hōei Eruption) during the Edo period. Hence statement 3 is incorrect.
- The 1707 eruption deposited ash as far as Edo (modern-day Tokyo).
- Mount Fuji is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, a zone of frequent earthquakes and volcanic activity.
- It is a symbol of Japan and a UNESCO World Heritage Site (2013) under the category “Cultural Site.” Hence statement 2 is correct.
- The Fuji Five Lakes region lies around its northern base — Yamanaka, Kawaguchi, Saiko, Shoji, and Motosu.
- Despite being dormant for centuries, Mount Fuji is still classified as an active volcano with potential for future eruptions.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2018) Q. Consider the following statements: 1. The Barren Island volcano is an active volcano located in the Indian territory. 2. Barren Island lies about 140 km east of Great Nicobar. 3. The last time the Barren Island volcano erupted was in 1991 and it has remained inactive since then. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 (c) 3 only (d) 1 and 3 |
9. With reference to the cultural history of India, consider the following statements:
1. Chhath Puja is the only Hindu festival that worships both the rising and setting Sun, symbolising life balance and gratitude.
2. Chhath Puja was recently inscribed on the UNESCO List of Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: Chhath Puja and politics: never the twain shall meet, say devotees
Chhath Puja:
- Chhath Puja is an ancient Vedic festival dedicated to Lord Surya (Sun God) and Chhathi Maiya, associated with the dawn goddess Usha.
- It is mainly celebrated in Bihar, Jharkhand, Eastern Uttar Pradesh, and Nepal’s Terai region.
- The word ‘Chhath’ means ‘sixth’, referring to the sixth day after Diwali, during Shukla Paksha of Kartika month (October–November).
- The festival spans four days —
1. Nahay Khay – Holy bathing and preparing sattvic food.
2. Kharna – Day-long fasting, followed by offering kheer and fruits to the Moon.
3. Sandhya Arghya – Offering prayers to the setting Sun.
4. Usha Arghya – Offering prayers to the rising Sun.
- Devotees perform ritual fasting, standing in water, and offering arghya (water and fruits) to the Sun.
- It is the only Hindu festival that worships both the rising and setting Sun, symbolising life balance and gratitude. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The rituals emphasize purity, discipline, and environmental consciousness — using natural offerings and clean water bodies.
- Offerings include thekua, sugarcane, rice, coconuts, and fruits.
- The festival has references in the Rig Veda and is linked to Karna, the son of Surya, from the Mahabharata.
- Recognised as an important folk and environmental festival, promoting community harmony and ecological respect.
Note: Chhath Puja is not yet inscribed on the UNESCO List of Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity (as of 2025). Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2024) Q. Which one of the following was the latest inclusion in the Intangible Cultural Heritage List of UNESCO? (a) Chhau dance (b) Durga puja (c) Garba dance (d) Kumbh mela |
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/cities/Delhi/chhath-puja/article70211168.ece
10. Consider the following pairs
| Wildlife | Naturally found in | |
| 1 | Blue-finned Mahseer | Cauvery River |
| 2 | Irrawaddy Dolphin | Chambal River |
| 3 | Rusty-spotted Cat | Eastern Ghats |
Which of the pairs given correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (c) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
1. Blue-finned Mahseer – Cauvery River – Correct
- The Blue-finned Mahseer (Tor khudree) is native to the Cauvery River system (mainly in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu).

2. Irrawaddy Dolphin – Chambal River – Incorrect
- The Irrawaddy Dolphin is found in brackish and coastal waters — especially in Chilika Lake (Odisha) and Sundarbans, not in the Chambal River.

3. Rusty-spotted Cat – Eastern Ghats – Correct
- The Rusty-spotted Cat (Prionailurus rubiginosus), the world’s smallest wild cat, is found in forests of Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats, and Central India.


