1. Consider the following statements with respect to nuclear power generation in India:
I. The Atomic Energy Act, 1962 enables Private and foreign participation in nuclear power generation in India.
II. The Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010 establishes a legal framework for liability and compensation in the event of a nuclear accident in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) I only
(b) II only
(c) Both I and I
(d) Neither I nor II
Answer: (b) II only
Explanation:
In NEWS: Government deliberating on questions of radioactive waste, private sector’s role in proposed nuclear bill
Nuclear Power Generation in India:
Atomic Energy Act, 1962 restricts nuclear power generation to government entities such as:
- NPCIL (Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited)
- BHAVINI (Bharatiya Nabhikiya Vidyut Nigam Limited)
- ASHVINI (NPCIL-NTPC JV). Hence statement I is incorrect.
- Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010 (CLND Act) — imposes operator and supplier liability, making foreign suppliers wary of participating. Hence statement II is correct.
- India is also a member of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and follows global nuclear safety norms.
- As of 2025, India operates 24 nuclear reactors with an installed capacity of around 7,480 MW, and several others are under construction.
- Nuclear energy currently contributes about 3% of India’s total electricity generation.
- India aims to increase nuclear capacity to 22,480 MW by 2031 and 100 GW by 2047 as part of its long-term clean energy strategy.
Three-Stage Nuclear Programme:
India’s indigenous nuclear power strategy, conceptualized by Dr. Homi J. Bhabha, is based on a three-stage plan:
Stage I – Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs): Use natural uranium as fuel and heavy water as moderator.
Stage II – Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs): Use plutonium produced from Stage I as fuel and generate more fissile material than they consume.
Stage III – Thorium-based Reactors (Advanced Heavy Water or Molten Salt Reactors): Utilize India’s vast thorium reserves to ensure long-term energy independence.
Proposed Changes in the Nuclear Energy Sector:
- Amendments to:
- Atomic Energy Act (1962)
- Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act (2010)
- To enable:
- Private and foreign participation in nuclear energy.
- Public–Private Partnerships (PPPs) in reactor design, construction, and operation.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2011) Q. The function of heavy water in a nuclear reactor is to (a) Slow down the speed of neutrons (b) Increase the speed of neutrons (c) Cool down the reactor (d) Both (a) and (c) |
2. Which of the following are functions of Regulatory T Cells (Tregs) in the human immune system?
1. Prevention of autoimmune diseases
2. Regulation of inflammatory responses
3. Maintenance of immune homeostasis
4. Facilitation of organ transplantation success
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Explanation:
In NEWS: Medicine Nobel for scientists who demystified the immune system
2025 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
Awarded for: Discoveries related to the role of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in immune tolerance
Laureates:
1. Shimon Sakaguchi (Japan)
2. Mary E. Brunkow (USA)
3. Fred Ramsdell (USA)
Key Discoveries:
1. Discovery of Regulatory T Cells (Tregs) – Shimon Sakaguchi (1995)
- Identified a unique subset of T cells (now known as Tregs) that prevent immune system overactivation.
- Challenged the earlier belief that self-reactive immune cells are eliminated solely in the thymus (central tolerance).
- Proposed peripheral tolerance via Tregs as a second layer of immune regulation.
2. FOXP3 Gene Discovery – Mary Brunkow & Fred Ramsdell (2001)
- Found that mutation in the FOXP3 gene causes immune dysregulation:
- In mice: “Scurfy” disease (severe autoimmune condition)
- In humans: IPEX syndrome (Immune dysregulation, Polyendocrinopathy, Enteropathy, X-linked)
- FOXP3 was identified as a master regulator gene for development and function of regulatory T cells.
3. Link Between FOXP3 and Tregs
Established that FOXP3 is essential for Treg development, thus connecting molecular genetics to immune regulation.
Importance of the Discovery:
Regulatory T Cells (Tregs) are vital in:
- Preventing autoimmune diseases
- Controlling inflammation
- Maintaining immune homeostasis
- Enabling successful organ transplantation
- Modulating immune response in cancer (where Tregs can suppress anti-tumor immunity)
Hence all are correct.
Applications in Medicine:
- Autoimmune diseases: Boosting Tregs could help treat lupus, Type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis.
- Organ transplantation: Tregs may help prevent graft rejection.
- Cancer treatment: Modulating Tregs to enhance immune attack on tumors.
- Chronic inflammation: Managing diseases like Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2022) Q. Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body? (a) They protect the body from environmental allergens. (b) They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation. (c) They act as immunosuppressants in the body. (d) They protect the body from the diseases caused by pathogens. |
3. Consider the following statements with respect to Mud Volcanoes:
1. They are often associated with tectonically active zones and hydrocarbon-rich sediments.
2. Unlike magmatic volcanoes, eruptions of Mud volcanoes are usually cool.
3. Baratang Mud Volcano located in the Andaman & Nicobar Islands is the only active mud volcano in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (d) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
In NEWS: GSI team to visit Andaman to investigate eruption at India’s only active mud volcano in Baratang
Baratang Mud Volcano:
- Located in Baratang Island, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, India about 100 km north of Port Blair.
- It emits mud, water, and methane gas, not molten lava.
- Height: ~3–4 meters, with small eruptions, especially during monsoon.
- It is surrounded by mangrove forests and limestone formations.
- It is located in a seismically active zone at the India–Burma plate boundary, associated with subduction zones, methane-rich sediments, and tectonic activity.
- It is the only active mud volcano in India. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- Eruptions may be triggered by earthquakes or plate movements.


Mud Volcanoes :
- A mud volcano is a geological structure where mud, water, and gases (mainly methane, carbon dioxide) erupt from underground.
- Unlike magmatic volcanoes, no molten lava is involved; eruptions are usually cool, and mostly mud flows. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- Often associated with tectonically active zones and hydrocarbon-rich sediments. Hence statement 1 is correct.
Examples
- Baratang Island, Andaman & Nicobar Islands – only active mud volcano in India.
- Balochistan, Pakistan – multiple mud volcanoes along the Makran coast.
- Azerbaijan (Gobustan) – known as “Land of Fire,” with hundreds of mud volcanoes.
- Trinidad & Tobago – mud volcanoes along fault lines.
- Indonesia & Taiwan – tectonically active mud volcano sites.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2018) Q. Consider the following statements: 1. The Barren Island volcano is an active volcano located in the Indian territory. 2. Barren Island lies about 140 km east of Great Nicobar. 3. The last time the Barren Island volcano erupted was in 1991 and it has remained inactive since then. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 (c) 3 only (d) 1 and 3 |
4. Which of the following organisms uses a distinctive “side-to-side sweeping motion” of the half-open beak in shallow water to catch fish?
(a) Painted stork
(b) Indian Nightjar
(c) White Ibis
(d) Common Myna
Answer: (a) Painted stork
Explanation:
In NEWS: ‘Kaziranga welcomes an old guest’: Assam celebrates return of painted storks after 4 years
Painted Stork:
- A large wading bird belonging to the stork family (Ciconiidae).
- Recognized by its pink tertial feathers, yellow beak, and white plumage with black markings.

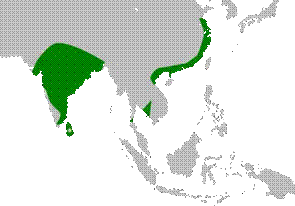
Habitat & Distribution
- Found in tropical Asia, mainly in India, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Myanmar, and parts of Southeast Asia.
- Prefers freshwater wetlands, marshes, lakes, floodplains, and shallow ponds.
- Often nests in large trees near water bodies — commonly seen with other colonial nesting birds like herons and ibises.
Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern (LC), though previously Near Threatened.
- CITES: Appendix II (trade controlled).
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule IV (protected species in India).
- Population trend: Increasing, though localized declines exist due to habitat loss and pollution.
Unique Features
- Feeding Habit: Uses a distinctive “side-to-side sweeping motion” of the half-open beak in shallow water to catch fish. Hence option (a) is correct.
- Colonial Nester: Breeds in large communal rookeries with other waterbirds, a sign of wetland health.
- Non-Migratory but Locally Nomadic: Moves seasonally in response to water availability.
- Ecological Role: Acts as a bio-indicator species of wetland ecosystem health.
Threats
- Wetland degradation and conversion to agriculture or urban land.
- Pollution and eutrophication and reducing fish populations.
- Disturbance at nesting sites and deforestation near wetlands.
| PYQ REFERENCE: Q. Which of the following organisms perform a waggle dance for others of their kin to indicate the direction and the distance to a source of their food? (2023) (a) Butterflies (b) Dragonflies (c) Honey Bees (d) Wasps Q. If you walk through countryside, you are likely to see some birds stalking alongside the cattle to seize the insects disturbed by their movement through grasses. Which of the following is/are such bird/birds? (2014) 1. Painted Stork 2. Common Myna 3. Black-necked Crane Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 only (c) 2 and 3 (d) 3 only |
5. Diethylene Glycol is a colorless, odorless, and hygroscopic organic compound.
It is a toxic alcohol used industrially as a solvent, antifreeze, and in the production of resins, plastics, and brake fluids. It is highly toxic to humans, especially when ingested. However, it has been found in some pharmaceutical formulations because
(a) It is approved by regulatory authorities as a safe pharmaceutical excipient.
(b) It enhances the flavor and color of syrups.
(c) It is a cheaper substitute for safe excipients like glycerin or propylene glycol.
(d) It helps in increasing the shelf life of the product and is used widely for that purpose.
Answer: (c) It is a cheaper substitute for safe excipients like glycerin or propylene glycol.
Explanation:
In NEWS: Coldrif cough syrup contamination linked to deaths of at least 16 children. Poor compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Good Laboratory Practices (GLP)
Diethylene Glycol (DEG -C₄H₁₀O₃):
- Diethylene Glycol (DEG) is a colorless, odorless, and hygroscopic organic compound.
- It is a toxic alcohol used industrially as a solvent, antifreeze, and in the production of resins, plastics, and brake fluids.
- DEG is highly toxic to humans, especially when ingested.
- It has been mistakenly used in pharmaceutical formulations, often as a cheaper substitute for safe excipients like glycerin or propylene glycol. Hence option (c) is correct.
Health Effects of DEG Poisoning:
- Toxic dose: As little as 1 ml/kg can be fatal.
- Target organs: Kidneys, liver, and central nervous system.
- Symptoms: Vomiting, Abdominal pain, Altered mental status, Acute kidney failure, Metabolic acidosis, Neurological complications and Death in severe cases
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2011) Q. Aspartame is an artificial sweetener sold in the market. It consists of amino acids and provides calories like other amino acids. Yet, it is used as a lowcalorie sweetening agent in food items. What is the basis of this use? (a) Aspartame is as sweet as table sugar, but unlike table sugar, it is not readily oxidized in human body due to lack of requisite enzymes. (b) When aspartame is used in food processing, the sweet taste remains, but it becomes resistant to oxidation. (c) Aspartame is as sweet as sugar, but after ingestion into the body, it is converted into metabolites that yield no calories. (d) Aspartame is several times sweeter than table sugar, hence food items made with small quantities of aspartame yield fewer calories on oxidation. |
6. Consider the following statements with respect to the IUCN World Conservation Congress:
I. The IUCN World Conservation Congress, 2025 was held in New Delhi, India.
II. India unveiled its first Red List in the 2025 Congress.
III. It is held once every two years.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) I only
(b) I and III
(c) II only
(d) II and III
Answer: (c) II only
Explanation:
In NEWS: India’s first Red List of Endangered Species to be unveiled at IUCN World Congress
IUCN World Conservation Congress:
- The IUCN World Conservation Congress (WCC) is a global forum for conservation and sustainable development.
- Organized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- Brings together governments, civil society organizations, Indigenous peoples, scientists, and businesses.
- It is held once every four years. Hence statement III is incorrect.
- Venue rotates globally; the 2025 Congress is in Abu Dhabi, UAE. Hence statement I is incorrect.
Objectives
- Set global conservation priorities.
- Evaluate the status of the world’s biodiversity and propose strategies for protection.
- Promote sustainable development policies and nature-based solutions.
- Facilitate international collaboration for biodiversity conservation and climate action.
India’s First Red List:
- Unveiled at the IUCN World Conservation Congress 2025 in Abu Dhabi.
- Marks India’s first national-level assessment of endangered species. Hence statement II is correct.
- Demonstrates India’s commitment to biodiversity conservation and global environmental responsibilities.
- Expected to guide national conservation priorities and policy actions.
- Covers species across flora and fauna within India.
- Aligns with IUCN methodology for global comparability.
- Provides a baseline for monitoring species population trends and habitat health.
Red List of Endangered Species:
- The Red List is a comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of species, assessing their risk of extinction.
- Maintained by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- Categorizes species as: Extinct, Extinct in the Wild, Critically Endangered, Endangered, Vulnerable, Near Threatened, Least Concern, Data Deficient, and Not Evaluated.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2011) Q. The “Red Data Books” published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) contain lists of 1. Endemic plant and animal species present in the biodiversity hotspots. 2. Threatened plant and animal species. 3. Protected sites for conservation of nature and natural resources in various countries. Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 and 3 (b) 2 only (c) 2 and 3 (d) 3 only |
7. With reference to the recent trends in India’s international trade (April–August 2025), which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. India’s services exports have grown at a higher rate than its merchandise exports.
2. Electronic goods have emerged as one of the fastest-growing export sectors for India.
3. India’s total exports combining merchandise and services have declined compared to the previous year.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: Export Surge: India Steps Up on Global Stage
India’s Export Growth (April–August 2025)
Overall Export Growth
- India’s total exports, combining merchandise and services, grew by 5.19% in the first five months of FY 2025–26 (April–August). Hence statement 3 is incorrect.
- The total value reached USD 346.10 billion, indicating resilience in global trade engagement.
Month-on-Month Growth
- In August 2025 alone, total exports rose by 4.77% compared to August 2024.
- Reflects steady recovery and positive trade momentum, even amid global uncertainties.
Merchandise vs Services Exports
- Merchandise exports: Increased by 2.31% in April–August 2025.
- India’s merchandise export to the USA was USD 6.87 billion in August 2025.
| India’s Merchandise Export to USA vs. other countries | ||
| India’s export destinations | July 2025 (In USD million) | August 2025 (In USD million) |
| USA | 8012.45 | 6865.47 ↓ |
| UAE | 2984.66 | 3245.26 ↑ |
| Netherlands | 1668.92 | 1829.77 ↑ |
| Australia | 495.65 | 554.67 ↑ |
| Nepal | 600.85 | 617.26 ↑ |
| South Africa | 611.28 | 654.58 ↑ |
| Hong Kong | 548.15 | 584.70 ↑ |
- Services exports: Rose significantly by 8.65%, underlining India’s strength in IT, business services, and consulting. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- India’s exports to Hong Kong, China, USA, Germany, Korea, UAE, Nepal, Belgium, Bangladesh, and Brazil have climbed the ladder of growth in April-August 2025 vs. April-August 2024.
Electronic Goods: Fastest-Growing Export Sector
- Electronic goods exports saw a massive 40.63% growth — the highest among all sectors. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- Driven by PLI scheme support, increased global demand, and mobile/device manufacturing exports.
Diversification of Export Base
- Non-petroleum, non-gems & jewellery exports increased by 7.76%, suggesting a broader, more stable export base.
- Reduces dependency on volatile commodity-linked sectors.
Top Performing Export Sectors
Significant growth observed in:
- Electronics
- Engineering goods
- Drugs and pharmaceuticals
- Textiles and apparel
- Agricultural and processed food products
- Indicates India’s growing capability in high-value manufacturing and agritech.
Key Government Schemes Supporting Exports
- RoDTEP (Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products): Refunds embedded taxes not rebated through other schemes.
- PLI (Production-Linked Incentive) Schemes: Boosts manufacturing in electronics, pharmaceuticals, textiles, etc.
- Districts as Export Hubs: Promotes local products through district-level identification and support.
- TIES (Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme): Improves export infrastructure like testing labs, cold chains, logistics.
Logistics & Trade Facilitation Initiatives
- National Logistics Policy: Reduces logistics costs, enhances competitiveness.
- PM GatiShakti: Unified digital platform for coordinated infrastructure planning across ministries.
- National Single Window System: Streamlines approvals and clearances for exporters.
- Trade Connect e-Platform: Enhances outreach and support for exporters via digital means.
GST Reform for Exporters (Effective 1st Nov 2025)
- 90% provisional GST refund to exporters of zero-rated supplies through a risk-based system.
- Rectification of inverted duty structure in selected sectors to reduce input tax burden.
Export Target for FY 2025–26
- India has set an ambitious export target of USD 1 trillion.
- As of August 2025, 34.61% of the target has already been achieved, indicating a strong performance trajectory.
New Trade Agreements
- India-UK Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA)
- India-EU Free Trade Agreement
- India-Australia Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement
- India-New Zealand Free Trade Agreement
- India and Oman Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
- India- Peru Free Trade Agreement (FTA)
- India- Chile Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
- India- UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2020) Q. With reference to the international trade of India at present, which of the following statements is/are correct? 1. India’s merchandise exports are less than its merchandise imports. 2. India’s imports of iron and steel, chemicals, fertilisers and machinery have decreased in recent years. 3. India’s exports of services are more than its imports of services. 4. India suffers from an overall trade/current account deficit. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 4 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 3 and 4 only |
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2175702
8. Mig La Pass, recently seen in the news for the construction of the world’s highest motorable road, is located in which one of the following mountain ranges?
(a) Karakoram Range
(b) Zanskar Range
(c) Pir Panjal Range
(d) Aravalli Range
Answer: (b) Zanskar Range
Explanation:
In NEWS: BRO Breaks Its Own Record, Builds World’s Highest Motorable Road at 19,400 ft in Ladakh
World’s Highest Motorable Road:
- Border Roads Organisation’s (BRO) Project Himank has constructed the world’s highest motorable road at Mig La Pass, located at an altitude of 19,400 feet in Ladakh.
- This surpasses BRO’s earlier record at Umling La (19,024 feet), set in 2021 and recognized by the Guinness World Records.
Strategic & Economic Importance:
- Part of the Likaru–Mig La–Fukche alignment, it creates a third key axis to Fukche, a border village.
- Enhances India’s border infrastructure and security posture.
- Expected to boost tourism in Ladakh, offering stunning Indus Valley views.
Mig La Pass:
- Mig La Pass is located in the eastern part of the Ladakh region of the Union Territory of Ladakh, India.
- It lies within the Himalayan mountain range, specifically in the Zanskar range, which is a sub-range of the greater Himalayas. Hence option (b) is correct.
- The region around Mig La Pass is characterized by rugged mountainous terrain with steep slopes, rocky outcrops, and sparse vegetation due to the high altitude.
- The climate is cold desert type, with temperatures often dropping well below freezing, especially in winter months. The pass remains snowbound for much of the year.
- Mig La serves as a critical mountain pass connecting the Likaru area to the west and Fukche village to the east, near the Line of Actual Control (LAC) between India and China.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2022) Q. Consider the following pairs: Peak Mountains 1. Namcha Barwa — Garhwal Himalaya 2. Nanda Devi — Kumaon Himalaya 3. Nokrek — Sikkim Himalaya Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched? (a) 1 and 2 (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 (d) 3 only |
9. Consider the following statements:
Statement I: During a supermoon, the moon appears larger up to 14% bigger and brighter up to 30% brighter than a typical full moon.
Statement II: The moon’s orbit around Earth is elliptical, causing variations in its distance.
Statement III: Supermoons can influence tidal forces slightly, leading to higher tides known as “perigean spring tides.”
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement II and Statement III are correct and both of them explain Statement I
(b) Both Statement II and Statement III are correct but only one of them explains Statement I
(c) Only one of the Statements II and III is correct and that explains Statement I
(d) Neither Statement II nor Statement III is correct
Answer: (b) Both Statement II and Statement III are correct but only one of them explains Statement I
Explanation:
In NEWS: What is a supermoon?


Supermoon:
- A supermoon occurs when a full moon coincides with the moon’s closest approach to Earth in its elliptical orbit, called perigee.
- During a supermoon, the moon appears larger (up to 14% bigger) and brighter (up to 30% brighter) than a typical full moon. Hence statement I is correct.
- The moon’s orbit around Earth is elliptical, causing variations in its distance; perigee is the nearest point, and apogee is the farthest. Hence statement II is correct and explains statement I
- Supermoons are visible to the naked eye and do not require telescopes or special equipment.
- These events are relatively rare and occur only when the timing of the full moon and perigee coincide.
- Supermoons can influence tidal forces slightly, leading to higher tides known as “perigean spring tides.” Hence statement III is correct but it is not the justification for statement I
- Supermoon events are often associated with cultural and religious festivals in many parts of the world.
- The next supermoon dates can be predicted and are published by astronomical organizations and observatories.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2013) Q. Consider the following phenomena: 1. Size of the sun at dusk 2. Colour of the sun at dawn 3. Moon being visible at dawn 4. Twinkle of stars in the sky 5. Polestar being visible in the sky Which of the above are optical illusions? (a) 1, 2 and 3 (b) 3, 4 and 5 (c) 1, 2 and 4 (d) 2, 3 and 5 |
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/what-is-a-supermoon/article70133754.ece
10. Consider the following kinds of organisms:
1. Copepods
2. Cyanobacteria
3. Diatoms
4. Foraminifera
Which of the above are primary producers in the food chains of oceans?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1 and 4 only
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Copepods are small crustaceans and consumers (zooplankton), not primary producers.
- Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic bacteria and primary producers.
- Diatoms are photosynthetic algae and primary producers.
- Foraminifera are protists that are mostly consumers (they feed on other microorganisms).
Hence option (b) is correct.

