1. With reference to the Great Nicobar Island Mega Project, consider the following statements:
1. The project includes development of an international transshipment port and a greenfield airport.
2. The project site is located near the Malacca Strait, giving it strategic maritime importance.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (c) Both 1 and 2
Explanation:
In NEWS: NGT gives clearance to Great Nicobar project

Great Nicobar Island Mega Project:
- The Great Nicobar Island mega project is a ₹92,000-crore infrastructure initiative of strategic and defence importance.
- The project includes an international transshipment port, a greenfield airport, a power plant, and township development. Hence statement 1 is correct
- The project site is located near the Malacca Strait, giving it strategic maritime importance. Hence statement 2 is correct
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) cleared the project and directed strict compliance with environmental clearance (EC) conditions.
- A High-Powered Committee (HPC) was formed to examine issues related to coral reefs, leatherback turtle nesting sites, and ecological concerns.
- The NGT noted that adequate environmental safeguards have been incorporated in the EC norms.
- Coral regeneration measures and shoreline protection were mandated to prevent erosion and protect biodiversity.
- The Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) for the project was conducted using one-season data, which was defended by the government.
- The tribunal observed that no part of the project area falls within Coastal Regulation Zone-IA (CRZ-IA).
- The project has faced opposition from local Scheduled Tribes such as the Nicobarese and Shompen over land rights issues.
- While environmental clearance has been upheld by the NGT, forest clearance issues are under challenge before the Calcutta High Court.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2014) Q. Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? (a) Andaman and Nicobar (b) Nicobar and Sumatra (c) Maldives and Lakshadweep (d) Sumatra and Java |
2. Consider the following pairs:
| S.no | Scheme | Primary Objective |
| 1. | AMRUT | Universal rural electrification |
| 2. | Swachh Bharat Mission Urban 2.0 | Garbage-free cities and solid waste management |
| 3. | Smart Cities Mission | Technology-driven urban development and smart governance |
| 4. | Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban) | Improvement of water supply and sewerage infrastructure |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: (c) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: Cities of debt
ULBs need more administrative capacity before they can tap the market
- The government’s updated ‘Urban Challenge Fund’ has rendered the attention of urban local bodies (ULB) an even more precious resource as they struggle to complete unfinished work under other schemes, including AMRUT, Swachh Bharat Mission Urban 2.0, ‘Smart Cities’, and Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, which also suffer from chronic underutilisation.
AMRUT (Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation)
- AMRUT was launched in 2015 by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- The mission aims to improve basic urban infrastructure such as water supply and sewerage systems. Hence pair 1 is incorrect
- AMRUT focuses on cities with a population of more than one lakh.
- AMRUT 2.0 aims to provide universal water supply coverage and improve sewerage management.
Swachh Bharat Mission – Urban (SBM-U 2.0)
- SBM-Urban 2.0 was launched in 2021 to achieve garbage-free cities. Hence pair 2 is correct
- The mission focuses on scientific solid waste management and source segregation of waste.
- Sustaining Open Defecation Free (ODF) status is one of its objectives.
- It includes plastic waste management and landfill remediation.
Smart Cities Mission
- Smart Cities Mission was launched in 2015 to improve urban quality of life through smart solutions. Hence pair 3 is correct
- It promotes area-based development such as retrofitting and redevelopment.
- Pan-city solutions using ICT-based governance are a key feature.
- One hundred cities were selected under the mission.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U)
- PMAY-Urban aims to achieve “Housing for All”. Hence pair 4 is incorrect
- It targets Economically Weaker Sections (EWS), Low Income Groups (LIG), and Middle Income Groups (MIG).
- Components include in-situ slum redevelopment and credit-linked subsidy scheme (CLSS).
- The scheme promotes affordable housing through partnerships and beneficiary-led construction.
3. With reference to the types of volcanic eruptions, consider the following pairs :
| S.No | Feature | Type of Eruption |
| 1 | Low viscosity lava | Effusive eruption |
| 2 | Pyroclastic flows | Explosive eruption |
| 3 | Violent eruption | Effusive eruption |
| 4 | Easy gas escape | Explosive eruption |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
Answer: (b) Only two
Explanation:
In NEWS: The Piton de la Fournaise volcano erupts in the southeast of the French overseas island of La Reunion on Sunday.
MainTypes of Volcanic eruptions:
Volcanic eruptions are generally classified as either effusive (gentle lava flows) or explosive (violent fragmentation of magma) based on magma viscosity and gas content.
| Feature | Effusive Eruption | Explosive Eruption |
| Magma Type | Basaltic (Mafic) | Andesitic/Rhyolitic (Felsic) |
| Viscosity | Low (Runny) | High (Sticky) |
| Gas Escape | Easy | Trapped |
| Energy | Gentle, oozing | Violent, blasting |
| Hazards | Lava flows | Ash clouds, pyroclastic flows |
Hence only two pairs are correctly matched.
Main Types of Volcanic Eruptions (Least to Most Explosive)
- Icelandic: Fissure eruptions with very thin, runny lava, covering large areas.
- Hawaiian: Effusive eruptions of low-viscosity basaltic lava, often producing lava fountains and flows.
- Strombolian: Moderate bursts of expanding gases that eject clots of incandescent lava, forming cinder cones.
- Vulcanian: Moderate to violent explosions, ejecting ash, blocks, and bombs.
- Pelean (or Peléan): Characterized by large, fast-moving pyroclastic flows caused by the collapse of a lava dome.
- Plinian: The most explosive type, involving sustained, violent ejection of gas and ash, creating massive eruption columns.
Other Eruption Classifications
- Phreatic: Steam-driven explosions caused by hot rock interacting with water, with no new magma involved.
- Phreatomagmatic: Direct interaction between magma and water (e.g., Surtseyan), producing fine ash.
- Submarine/Subglacial: Eruptions occurring underwater or under ice.
Piton de la Fournaise Volcano:
- Piton de la Fournaise (‘Peak of the Furnace’) is a shield volcano on the eastern side of Réunion island, a French overseas department and region, in the Indian Ocean.
- The Piton de la Fournaise is one of the most active volcanoes in the world.
- Since 2010, it has been part of the Réunion National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- As of February 17, 2026, the volcano is currently in a state of active eruption, marking its second eruptive event of the year.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2024) Q. Consider the following : 1. Pyroclastic debris 2. Ash and dust 3. Nitrogen compounds 4. Sulphur compounds How many of the above are products of volcanic eruptions? (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) Only three (d) All four |
Source: The Hindu
4. Consider the following statements with respect to the UPI One World Wallet Service:
- It allows international travellers to make UPI payments in India without an Indian bank account.
- The service requires foreign travellers to have an Indian mobile number.
- It has a maximum limit of ₹25,000 per transaction.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (b) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: NPCI extends ‘UPI One World’ wallet service to visitors from 40 countries to AI Summit
‘UPI One World’ wallet service:
- The UPI One World wallet is a digital prepaid payment instrument (PPI) launched by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) for international travellers and Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) visiting India.
- It enables foreign travellers to make real‑time Person‑to‑Merchant (P2M) UPI payments across India without requiring an Indian bank account or an Indian mobile number. Hence statement 1 is correct and 2 is incorrect.
- Users can pay merchants by scanning UPI QR codes, just like Indian residents do, using the “Made in India” UPI digital payment system.
- The‘UPI One World’ wallet service is available to visitors and delegates from over 40 countries attending the AI summit.
- Visitors can register via authorised prepaid payment instrument (PPI) issuers, such as through the CheqUPI app by Transcorp downloaded from the Play Store/App Store.
- They complete a simple KYC process (passport, visa details, selfie).
- After setup, a unique UPI ID is generated, and users can load money using international debit/credit cards.
- Each load is capped at a certain limit per transaction and per month under RBI/foreign‑exchange norms.
- Transaction Limits:
- Max per transaction: ₹25,000. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- Monthly cap: ₹50,000.
- Any unused balance can be refunded to the original payment source when the trip ends.
- This pilot showcases India’s digital payment infrastructure and makes cashless payments easier for global visitors.
- It aims to reduce dependence on cash and simplify foreign travellers’ spending in India during major events.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2017) Q. Which of the following is a most likely consequence of implementing the Unified Payments Interface (UPI)? (a) Mobile wallets will not be necessary for online payments. (b) Digital currency will totally replace the physical currency in about two decades. (c) FDI inflows will drastically increase. (d) Direct transfer of subsidies to poor people will become very effective. |
5. The Andromeda Galaxy was recently in the news because:
(a) It was observed undergoing a supernova explosion before forming a neutron star
(b) It collapsed directly into a black hole without a supernova explosion
(c) It formed a new planetary system similar to the Solar System
(d) It was the first exoplanet detected outside the Milky Way
Answer: (b) It collapsed directly into a black hole without a supernova explosion
Explanation:
In NEWS: Scientists capture clearest evidence yet of star collapsing into black hole
- Scientists observed a massive star in the Andromeda Galaxy collapsing directly into a black hole. Hence option (b) is correct.
- The star disappeared without undergoing a typical supernova explosion.
- The phenomenon is known as direct collapse, where a massive star turns into a black hole without a visible explosive event.
- The event was identified using archival infrared data from NASA’s NEOWISE telescope.
- The star showed gradual infrared brightening for about three years before fading and disappearing.
- The collapse left behind a shell of dust, indicating stellar material ejection without a supernova.
- The Andromeda Galaxy is located approximately 2.5 million light-years away from Earth.
- The findings were published in the journal Science (February 2026).
- Direct collapse events provide rare observational evidence for alternative black hole formation pathways.
Andromeda Galaxy:
- The Andromeda Galaxy is the nearest large spiral galaxy to the Milky Way.
- It is also known as Messier 31 (M31).
- Located about 2.5 million light-years from Earth. Visible to the naked eye under dark sky conditions.
- Part of the Local Group of galaxies, which includes:
- Milky Way
- Triangulum Galaxy (M33)
- Several dwarf galaxies.
- Andromeda is slightly larger than the Milky Way and contains hundreds of billions of stars.
- It is moving toward the Milky Way and is expected to collide/merge with it in about 4–5 billion years.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2015) Q. The term ‘Goldilocks Zone’ is often seen news in the context of (a) the limits of habitable zone above the surface of the Earth (b) regions inside the Earth where shale gas is available (c) search for the Earth-like planets in outer space (d) search for meteorites containing precious metals |
6. Which of the following government initiatives are related to promoting circular economy in agriculture and allied sectors?
1. GOBARdhan Scheme
2. Crop Residue Management (CRM)
3. Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
4. Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF)
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Explanation:
In NEWS: Circular Economy in Agriculture: Waste to Wealth
Government Initiatives Driving Circular Agriculture:
- Circular agriculture promotes converting agricultural and allied sector waste into valuable resources such as energy, organic manure, and bio-inputs.
- The “waste-to-wealth” approach focuses on resource recovery, reuse, recycling, and value addition.
- Circular agriculture aligns with Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 2 related to food security and sustainable agriculture.
1. GOBARdhan (Galvanising Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan)
- GOBARdhan aims to convert cattle dung, crop residues, and food waste into compressed biogas (CBG) and organic manure.
- The Unified GOBARdhan Portal was launched to improve transparency and monitoring.
- Compressed biogas (CBG) under the scheme has been included in carbon credit trading mechanisms.
- ICAR has developed crop-specific guidelines for using biogas slurry to improve soil health.
2. Crop Residue Management (CRM)
- CRM promotes both in-situ and ex-situ management of crop residues.
- In-situ management includes incorporating residues directly into soil or using them as mulch.
- Ex-situ management involves using residues for composting, bioenergy, or biogas production.
- Custom Hiring Centres (CHCs) provide farmers access to crop residue management machinery.
3. Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
- AIF was launched in 2020-21 to provide medium to long-term credit for post-harvest infrastructure.
- Beneficiaries include FPOs, PACS, agri-entrepreneurs, and organic farmers.
- Infrastructure supported includes warehouses, cold storage, sorting and grading units, and processing centres.
4. Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF)
- AHIDF was launched under Atmanirbhar Bharat with a corpus of ₹15,000 crore.
- It promotes investments in dairy processing, animal feed manufacturing, and waste-to-wealth initiatives.
- The scheme encourages converting livestock waste into organic fertilizers and biogas.
5. Jal Shakti Mission & Water Reuse
- The Ministry of Jal Shakti promotes reuse of treated wastewater for agriculture, landscaping, and horticulture.
- Jal Shakti initiatives include watershed development, rainwater harvesting, and groundwater recharge.
- Jal Jeevan Mission aims to provide functional household tap water connections supplying 55 LPCD of drinking water in rural areas.
Hence all the statements are correct.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2025) Q. Consider the following statements: Statement I: Circular economy reduces the emissions of greenhouse gases. Statement II: Circular economy reduces the use of raw materials as inputs. Statement III: Circular economy reduces wastage in the production process. Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements? (a) Both Statement II and Statement III are correct and both of them explain Statement I (b) Both Statement II and Statement III are correct but only one of them explains Statement I (c) Only one of the Statements II and III is correct and that explains Statement I (d) Neither Statement II nor Statement III is correct |
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2228963®=3&lang=1
7. How many of the following are the features of Bhirrana, one of the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) sites?
1. Subterranean dwelling pits
2. Evidence of bead manufacturing
3. Planned streets and early drainage systems
4. Hakra Ware pottery
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
Answer: (d) All four
Explanation:
In NEWS: Indus Valley Civilisation May Date Back 8,000 Years
- The Indus Valley Civilisation may be far older than previously thought, with cultural layers dating back to ~8000 years.
- This evidence comes from Bhirrana, one of the earliest Indus‑related archaeological sites.
- This could reshape understanding of the evolution of urban societies in South Asia relative to other early civilisations like ancient Egypt.
Bhirrana:
- Bhirrana, located in Haryana’s Fatehabad district along the dried-up Sarasvati River, is a critical Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) excavated site, recognized as the oldest (>7500 BCE) Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) site, predating Mehrgarh.
- It is excavated by the ASI under the direction of L.S. Rao, revealing a 4.20-meter-thick deposit.
- Cultural Sequence:
- Period I-A (Hakra Ware Culture): Features subterranean dwelling pits, Hakra pottery, beads, copper bangles, and bone points. Hence 1 and 4 are correct.
- Period I-B (Early Harappan): Characterized by mud-brick houses (ratio 1:2:3), Kalibangan-I pottery, and a four-foil shaped seal.
Key Finds:
- “Dancing Girl” Graffiti: A pottery shard with a drawing similar to the famous bronze statue from Mohenjo-daro.
- Early evidence of bead manufacturing, copper/bronze tools, and advanced, fired bricks. Hence 2 is correct.
- Evidence of planned streets and early drainage systems. Hence 3 is correct.
- The site provides evidence of, indigenous evolution from the Hakra culture to the mature Harappan phase.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2013) Q. Which of the following characterizes/ characterize the people of Indus Civilization? 1. They possessed great palaces and temples. 2. They worshipped both male and female deities. 3. They employed horse-drawn chariots in warfare. Select the correct statement/ statements using the codes given below. (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 only (c) 1, 2 and 3 (d) None of the statements given above is correct |
8. Consider the following statements with reference to the K‑9 Vajra-T howitzer:
I. It is manufactured in India with technology transfer from South Korea.
II. It can operate in diverse terrains, including deserts and high-altitude areas.
III. It can engage targets up to about 40 km with standard ammunition.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I and II only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
Answer: (d) I, II and III
Explanation:
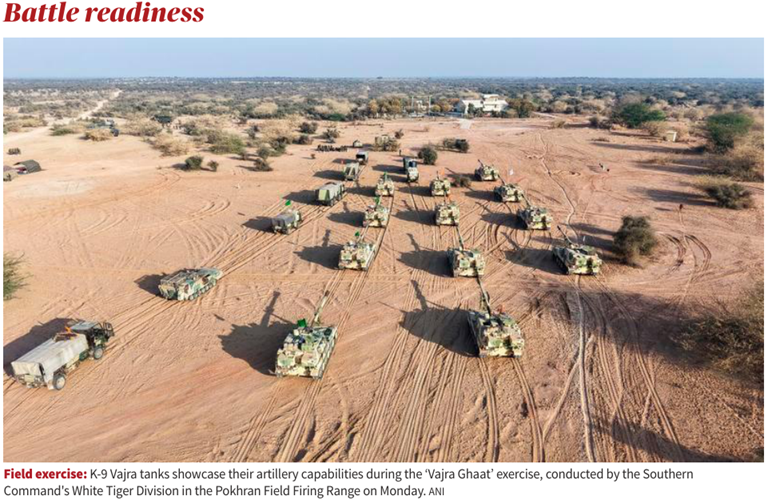
In NEWS: K-9 Vajra tanks showcase their artillery capabilities during the ‘Vajra Ghaat’ exercise, conducted by the Southern Command’s White Tiger Division in the Pokhran Field Firing Range.
k-9 vajra Tanks:
- The K9 Vajra-T is a 155 mm/52-calibre tracked self-propelled howitzer customized by Larsen & Toubro for the Indian Army from the South Korean K9 Thunder. Hence statement I is correct.
- It is designed for long-range, high-accuracy precision fire in diverse terrains, including deserts and high-altitude areas. Hence statement II is correct.
- Following successful deployment of the first 100 units, India ordered additional units in 2024, enhancing the army’s firepower and mobility.
- It is capable of engaging targets up to ~40 km with standard and specialized ammunition. Hence statement III is correct.
- It features a semi-automatic feeding system, capable of a 3-round burst in 30 seconds or 15 rounds in 3 minutes.
- It is equipped with a 1,000 HP engine, achieving speeds up to 67 km/h with a 480 km operating range.
- It is engineered to operate effectively in sub-zero temperatures.
- The K‑9 Vajra provides mobile artillery support that can keep pace with mechanised armoured formations, something towed artillery cannot do effectively.
- Its mobility and firepower make it a crucial component for modern artillery doctrine, enhancing India’s ability to conduct deep fires and rapid manoeuvre.

| PYQ REFERENCE: (2025) Q. With reference to India’s defence, consider the following pairs: Aircraft Type Description I. Dornier-228 – Maritime patrol aircraft II. IL-76 – Supersonic combat aircraft III. C-17 Globemaster III – Military transport aircraft How many of the pairs are correctly matched? (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) All three (d) None |
Source: The Hindu
9. Consider the following statements regarding applications of drones in India:
1. Drones are used for land and property surveys under the SVAMITVA Scheme.
2. Drones assist in precision agriculture including spraying fertilisers and pesticides.
3. Drones are used for infrastructure monitoring such as highways and railway tracks.
4. Drones help in disaster management through aerial surveillance and real-time assessment.
5. Drones are used for delivery of medicines and healthcare logistics in remote areas.
6. Drones are used for security surveillance and crowd monitoring.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only three
(b) Only four
(c) Only five
(d) All six
Answer: (d) All six
Explanation:
In NEWS: India’s Drone Ecosystem – From Policy to Public Service Transformation
India’s Drone Ecosystem:
- India has developed a regulated drone ecosystem supported by policy reforms and digital governance.
- As of February 2026, more than 38,500 drones have been registered with Unique Identification Numbers (UIN).
- Around 39,890 DGCA-certified remote pilots are operational in India.
- The DGCA has approved 244 Remote Pilot Training Organisations (RPTOs).
Policy and Regulatory Framework
- The Drone Rules, 2021 simplified procedures and reduced regulatory barriers.
- Application forms were reduced from 25 to 5, and approval requirements reduced from 72 to 4.
- Nearly 90% of Indian airspace has been designated as Green Zone allowing flights up to 400 feet.
- Civilian drone operations are permitted for drones weighing up to 500 kg.
- Traditional pilot licence requirements were replaced with Remote Pilot Certificates issued by DGCA.
- The Digital Sky Platform provides a single-window system for drone operations.
- Regulatory services such as registration and certification have migrated to the eGCA platform.
Applications of Drones in India:
- Drones are used for precision agriculture including crop monitoring and pesticide spraying.
- Drones support PMFBY crop damage assessment and yield estimation.
- Drones enable SVAMITVA land surveys for property mapping and issuing property cards.
- Drones assist in infrastructure monitoring such as highways, bridges, and railway tracks.
- Drones help in disaster management through real-time aerial surveillance and rescue coordination.
- Drones are deployed for border surveillance and defence reconnaissance.
- Drones assist law enforcement in crowd monitoring and traffic management.
- Drones are used in railway security surveillance by the Railway Protection Force (RPF).
- Drones support environmental monitoring, including forest cover and wildlife tracking.
- Drones enable urban planning and smart city mapping.
- Drones assist in mining inspection and monitoring illegal activities.
- Drones are used for delivery of medicines and healthcare logistics in remote areas.
- Drones help in powerline inspection and energy infrastructure monitoring.
- Drones support aerial photography, surveying, and geospatial mapping.
- Drones enhance coastal security and maritime surveillance.
Hence all the statements are correct.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2020) Q. Consider the following activities: 1. Spraying pesticides on a crop field 2. Inspecting the craters of active volcanoes 3. Collecting breath samples from spouting whales for DNA analysis At the present level of technology, which of the above activities can be successfully carried out by using drones? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2228954®=3&lang=1
10. Consider the following statements:
1. There are no parables in Upanishads.
2. Upanishads were composed earlier than the Puranas.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
- The Upanishads frequently use parables, allegories, and illustrative stories to explain complex philosophical concepts like Atman and Brahman.
- Famous examples include the parable of the “Two Birds” (Mundaka Upanishad), the story of Nachiketa and Yama (Katha Upanishad), and the dialogue of Svetaketu (Chandogya Upanishad). Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- Chronologically, the principal Upanishads were composed during the Late Vedic period (c. 800–400 BCE).
- In contrast, the Puranas were compiled and reached their current form much later, primarily between the 3rd and 16th centuries CE. Hence statement 1 is correct.

