1. With reference to Indian Judiciary, consider the following statements:
1. According to Article 124, every judge of the Supreme Court shall be appointed by the President by warrant under his hand and seal.
2. According to the constitution of India, the seniormost Judge of the Supreme Court considered fit to hold the office should be appointed as the Chief Justice of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (a) 1 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: Justice Surya Kant to take over as 53rd Chief Justice of India on November 24
Appointment of Supreme Court Judges:
- The Chief Justice of India and the Judges of the Supreme Court are appointed by the President under clause (2) of Article 124 of the Constitution. Hence statement 1 is correct.
CHIEF JUSTICE OF INDIA :
- Appointment to the office of the Chief Justice of India should be of the seniormost Judge of the Supreme Court considered fit to hold the office. The Union Minister of Law, Justice and Company Affairs would, at the appropriate time, seek the recommendation of the outgoing Chief Justice of India for the appointment of the next Chief Justice of India.
1. Whenever there is any doubt about the fitness of the seniormost Judge to hold the office of the Chief Justice of India, consultation with other Judges as envisaged in Article 124 (2) of the Constitution would be made for appointment of the next Chief Justice of India.
2. After receipt of the recommendation of the Chief Justice of India, the Union Minister of Law, Justice and Company Affairs will put up the recommendation to the Prime Minister who will advise the President in the matter of appointment.
- According to Article 124, every judge of the Supreme Court shall be appointed by the President by warrant under his hand and seal after consultation with such Judges of the Supreme Court and of the High Courts in the States as the President may deem necessary for this purpose.
- S/he shall hold office until the age of 65 years, provided that in the case of appointment of a Judge other than the Chief Justice, the Chief Justice of India shall always be consulted.
Qualifications:
- A person shall not be qualified for appointment as a Judge of the Supreme Court unless,
- She/he is a citizen of India and has been for at least five years a Judge of a High Court or of two or more such Courts in succession; or has been for at least ten years an advocate of a High Court or of two or more such Courts in succession; or is, in the opinion of the President, a distinguished jurist.
- The senior most judge was surpassed for the appointment as the Chief Justice of India 3 times in the history of the Supreme Court of India.
- It is customary, and not law, that the most senior judge of the Supreme Court, at the time when the current Chief Justice of India (CJI) retires, becomes the next CJI. The seniority is measured by the length of service on the Supreme Court. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
- The first time this convention was breached was in February 1964, when Gajendragadkar J superseded Imam J, who was seriously unwell.
- The second breach was when A.N. Ray J was appointed as the CJI on April 25, 1973, by superseding three senior-most judges (Shelat, Hegde and Grover JJ). The supersession was made on the day following the Supreme Court’s judgment in Keshavanada Bharati v State of Kerala.
- The custom was sidestepped for a third time in 1977 when M H Beg J superseded H R Khanna J. When the first Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of India, Harilal Kania J, passed away in 1951, on hearing the rumour that the government is contemplating appointing somebody other than the senior-most justice, all the judges threatened to resign if the seniority norm was not followed.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2021) Q. With reference to Indian Judiciary, consider the following statements: 1. Any retired judge of the Supreme Court of India can be called back to sit and act as a Supreme Court judge by the Chief Justice of India with prior permission of the president of India. 2. A High Court in India has the power to review its own judgement as the Supreme Court does. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
2. Regarding ‘The National Beekeeping and Honey Mission (NBHM)’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. The National Beekeeping and Honey Mission (NBHM) is a Central Sector Scheme launched by the Government of India.
2. The scheme NBHM is being implemented by the National Bee Board (NBB).
3. As per the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA), India is the second largest exporter of honey, after China
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (d) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
In NEWS: National Beekeeping & Honey Mission – Bringing Sweet Revolution: Buzzing for a Better India

The National Beekeeping and Honey Mission (NBHM)
- The National Beekeeping and Honey Mission (NBHM) is a Central Sector Scheme launched by the Government of India for the overall promotion and development of scientific beekeeping and the production of quality honey and other beehive products. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Implemented through the National Bee Board (NBB), the scheme was announced under the banner of Atmanirbhar Bharat with a total budget outlay of ₹500 crore for three years (FY 2020–21 to 2022–23). Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It has since been extended for another three years (FY 2023–24 to 2025–26) with a remaining budget of ₹370 crore from the original allocation.
- Beekeeping, an agro-based activity undertaken by farmers and landless labourers in rural areas, forms an integral part of the Integrated Farming System.
- Integrated farming (or integrated agriculture) is a commonly and broadly used word to explain a more integrated approach to farming as compared to existing monoculture approaches. It refers to agricultural systems that integrate livestock, fisheries, crop production, horticulture, etc.
- It plays a crucial role in pollination, thereby enhancing crop yields and farmers’ income while providing honey and other high-value beehive products such as beeswax, bee pollen, propolis, royal jelly, bee venom, etc., all of which serve as important sources of livelihood for rural communities.
Export of Natural Honey from India:
- India exports a variety of natural honey like Rapeseed/Mustard Honey, Eucalyptus Honey, Lychee Honey, Sunflower Honey, etc.
- Major Indian states producing honey are: Uttar Pradesh (17%), West Bengal (16%), Punjab (14%), Bihar (12%) and Rajasthan (9%).
- India exported around 1.07 lakh metric tonnes (MT) of natural honey worth USD 177.52 million in FY 2023-24.
- Major export destinationsincluded the U.S.A, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar and Libya.
- As per the July 2025 Monthly Dashboard for Honey, prepared jointly by the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) and Crisil, globally, India is the second largest exporter of honey, after China, as of marketing year 2024, up from the 9th rank in 2020. Hence statement 3 is correct.
National Bee Board (NBB)
- National Bee Board was registered as a society under Societies Registration Act XXI of 1860, on July 19, 2000, and was reconstituted under the Chairmanship of Secretary (A&C) in June, 2006.
- The main objective of NBB is overall development, promotion of scientific beekeeping in the country to increase the productivity of crops through pollination and increase the honey production for increasing the income of the beekeepers/farmers.
- NBB has been designated/recognized as Nodal Agency for overall development/promotion of scientific beekeeping in the country.
- The scheme NBHM is being implemented by NBB.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2012) Q. How does the National Rural Livelihood Mission seek to improve livelihood options of rural poor? 1. By setting up a large number of new manufacturing industries and agribusiness centres in rural areas 2. By strengthening ‘self-help groups’ and providing skill development 3. By supplying seeds, fertilizers, diesel pump-sets and micro-irrigation equipment free of cost to farmers Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2185400
3. Consider the following pairs:
| S.no | UNESCO’s designated Creative City | Field |
| 1 | Jaipur | Crafts & Folk Art |
| 2 | Chennai | Film |
| 3 | Mumbai | Music |
| 4 | Lucknow | Gastronomy |
How many of the Pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
Answer: (b) Only two
Explanation:
In NEWS: Lucknow declared UNESCO ‘Creative City of Gastronomy’
Lucknow – UNESCO Creative City of Gastronomy (2025)
- Lucknow has been designated as a UNESCO Creative City of Gastronomy in October 2025.
- The recognition was announced at the 43rd UNESCO General Conference in Samarkand, Uzbekistan.
- Lucknow is the second Indian city to receive this title — after Hyderabad (recognized in 2019).
- The nomination was submitted by the Uttar Pradesh Directorate of Tourism through the Union Ministry of Culture.
- The city joins the UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN), which promotes culture-based sustainable urban development.
Why Lucknow Was Selected
- Lucknow is historically known as the City of Nawabs and the heart of Awadhi cuisine.
- It represents a blend of royal culinary traditions and inclusive street food culture.
- Signature dishes include Galouti Kebabs, Awadhi Biryani, Tokri Chaat, Makhan Malai, Sheermal, and Nihari.
- The cuisine reflects cultural harmony, combining Hindu and Mughal culinary practices.
- The city maintains a living food ecosystem — from heritage royal kitchens to small vendors and family-run eateries.
About the UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN)
- Established by UNESCO in 2004 to promote cooperation among cities using culture and creativity as drivers of sustainable development.
- Covers 7 fields: Literature, Music, Crafts & Folk Art, Design, Media Arts, Film, and Gastronomy.
- As of 2025, 350+ cities are part of the UCCN.
- In India, member cities include:
- Jaipur – Crafts & Folk Art
- Varanasi – Music
- Chennai – Music
- Hyderabad – Gastronomy
- Mumbai – Film
- Srinagar – Crafts & Folk Art
- Gwalior – Music
- Kozhikode – Literature
- Lucknow – Gastronomy (2025 addition)
Hence 1 and 4 are correctly matched.
Significance of the Recognition
- Promotes cultural diplomacy and soft power through cuisine and heritage.
- Enhances food tourism and local economic development.
- Encourages sustainable urban development through culinary heritage preservation.
- Supports women entrepreneurs and small-scale food vendors in the local food ecosystem.
- Highlights Awadhi cuisine on the global culinary map.
- Aligns with India’s initiatives under Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav and Dekho Apna Desh.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2024) Q. Consider the following properties included in the World Heritage List released by UNESCO: 1. Shantiniketan. 2. Rani-ki-Vav 3. Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysalas 4. Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodhgaya How many of the above properties were included in 2023? (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) Only three (d) All four |
4. Which among the following best describes the term ‘Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO)’ ?
(a) A circular orbit above the equator where a satellite appears stationary relative to the Earth.
(b) An elliptical orbit used to transfer a satellite from low Earth orbit (LEO) to geostationary orbit (GEO).
(c) An orbit in which a satellite passes over both poles during each revolution.
(d) A medium Earth orbit primarily used for navigation satellites like NavIC or GPS.
Answer: (b) An elliptical orbit used to transfer a satellite from low Earth orbit (LEO) to geostationary orbit (GEO).
Explanation:
In NEWS: ISRO launches advanced GSAT-7R, India’s heaviest communication satellite
GSAT-7R:
- GSAT-7R is an Indian military communication satellite developed by ISRO.
- It is intended to provide secure real-time communication for the Indian Navy.
- Serves as an upgrade to GSAT-7, enhancing network-centric operations and data sharing among naval assets.
- Operates in Geostationary Orbit (GEO) to cover wide oceanic regions.
- Part of India’s strategic defense satellite program for secure military communications. Hence option (b) is correct.
Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO):
- Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) is an elliptical Earth orbit used to transfer a satellite from low Earth orbit (LEO) to a geosynchronous orbit (GEO).
- It serves as an intermediate orbit — a stepping stone for satellites to reach their final circular geosynchronous orbit (~35,786 km altitude).
- A launch vehicle places the satellite in GTO; the satellite then uses its onboard propulsion system (apogee kick motor) to circularize the orbit at geosynchronous altitude.
Other important Space orbitals:
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO) – 160–2,000 km above Earth, ~90–120 min orbit; used for Earth observation, remote sensing, ISS, small satellites.
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) – 2,000–35,786 km altitude, 2–12 hr orbit; mainly for navigation satellites like GPS, Galileo, NavIC.
- Geosynchronous Orbit (GSO) – 24-hour orbital period matching Earth’s rotation; satellite returns to same sky position daily.
- Geostationary Orbit (GEO) – Circular GSO above equator at 35,786 km; satellite appears stationary, used for TV, communication, weather.
- Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) – Elliptical orbit from LEO → GEO with perigee ~250–300 km and apogee ~35,786 km; used for satellite deployment.
- Polar Orbit – Passes over both poles, ~700–800 km altitude; covers the whole Earth over time, used for mapping, reconnaissance, environmental monitoring.
- Sun-Synchronous Orbit (SSO) – Special polar orbit maintaining constant local solar time; used for uniform lighting in imaging satellites.
- Hohmann Transfer Orbit – Energy-efficient transfer orbit between two circular orbits; basis for LEO → GTO → GEO transitions.
- Escape Velocity – Minimum speed to break free from Earth’s gravity, ~11.2 km/s; used in interplanetary missions.
- Lagrange Points (L1–L5) – Points where Earth’s and Sun’s gravity balance; ideal for space observatories and missions like Aditya-L1.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2011) Q. Satellites used for telecommunication relay are kept in a geostationary orbit. A satellite is said to be in such as orbit when: 1. The orbit is geosynchronous. 2. The orbit is circular. 3. The orbit lies in the plane of the earth’s equator. 4. The orbit is at an altitude of 22,236 km. Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1, 2 and 3 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only (c) 2 and 4 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
5. Which of the following statements about Chabahar Port is/are correct?
1. It is located in Iran on the Gulf of Oman.
2. It provides India direct access to Afghanistan and Central Asia bypassing Pakistan.
3. It is part of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: India gets six-month waiver on U.S. sanctions against Chabahar: MEA
Chabahar Port
- Location: Southeastern Iran, on the Gulf of Oman, near the Iranian-Indian border with Pakistan. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Type: Deep-sea port, free-trade and transit hub.
- Strategic Importance:
- Provides India direct access to Afghanistan and Central Asia bypassing Pakistan. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- Counterbalances China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
- Enhances trade in the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC). Hence statement 3 is incorrect.
- Development: India and Iran signed agreements to develop and operate two berths at Chabahar. India has invested in terminal construction, connectivity infrastructure, and port equipment.
- Connectivity: Linked to Zaranj in Afghanistan via road; can connect to Central Asia for trade.
- Geopolitical Aspect: Strengthens India-Iran ties, reduces dependence on Pakistani ports, and provides access to energy and mineral resources in Afghanistan and Central Asia.
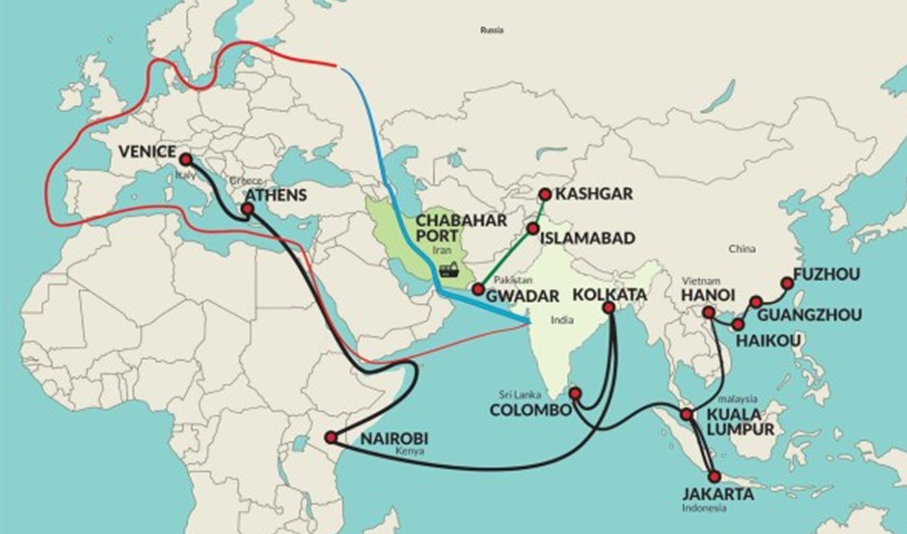
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2023) Q. Consider the following pairs : Port – Well known as 1. Kamarajar Port – First major port in India registered as a company 2. Mundra Port – Largest privately owned port in India 3. Visakhapatnam – Largest container port in India How many of the Pairs given above are correctly matched? (a) Only one pair (b) Only two pairs (c) All three pairs (d) None of the pairs |
6. Consider the following statements:
I. The Swadesh Darshan aims to develop theme-based tourist circuits, while PRASHAD Scheme aims to develop pilgrimage and heritage destinations in India.
II. Both the Swadesh Darshan and PRASHAD schemes are the Central Sector Scheme.
III. Both the Swadesh Darshan and PRASHAD schemes are implemented by the Ministry of Tourism.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All the three
(d) None
Answer: (c) All the three
Explanation:
In NEWS: Sardar Patel’s vision and the meaning of national unity today
Swadesh Darshan Scheme
- Type: Central Sector Scheme.
- Objective: Promote integrated development of theme-based tourist circuits in India to boost tourism and local economy.
- Launch Year: 2014.
- Implementing Ministry: Ministry of Tourism.
- Key Features:
- Focus on theme-based circuits like Spiritual, Buddhist, Eco, Coastal, Wildlife, Heritage, Desert, Himalayan, Tribal, North-East, and Rural circuits.
- Funding: Central share up to 60% of project cost in general areas, 90% in North-Eastern and hilly states.
- Includes infrastructure development, tourism facilities, and skill development.
PRASHAD Scheme
- Full Form: Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive
- Type: Central Sector Scheme.
- Objective: Integrated development of pilgrimage and heritage destinations in India.
- Launch Year: 2014.
- Implementing Ministry: Ministry of Tourism.
- Key Features:
- Focus on infrastructure development, amenities, and beautification of pilgrimage sites.
- Promote heritage conservation and cultural tourism.
- Funding pattern similar to Swadesh Darshan.
Hence all the statements are correct.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (UPPSC 2017) Q. Swadesh Darshan Scheme launched by Government of India does not include development of which of the following tourist circuits? (a) Heritage circuit (b) Sufi circuit (c) Ramayan circuit (d) All of the above are part of the tourism circuit |
7. Consider the following statements:
Statement I: Exercise Trishul 2025 is a tri-service military exercise conducted along western India.
Statement II: It is named ‘Trishul’ because the exercise is conducted between India, Pakistan and Afghanistan.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement II is correct
Answer: (c) Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
Explanation:
In NEWS: Tri-services ‘Trishul 2025’ to begin on November 3, set to strengthen joint combat preparedness
Exercise Trishul 2025:
- Exercise Trishul 2025 is a tri-service military exercise involving the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- The exercise is led by the Indian Navy.
- It is conducted along western India, including Rajasthan, Gujarat coast, Sir Creek, and the northern Arabian Sea.
Hence Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
Objectives:
- Its main objective is to test joint operations and multi-domain warfare, including land, sea, air, cyber, and electronic warfare.
- It aims to enhance inter-service coordination and overall operational readiness.
- The exercise demonstrates indigenous capabilities and India’s deterrence posture.
- It strengthens western front defense, maritime security in the Arabian Sea, and integrated theater command preparedness.
8. Which of the following statements about Rare Earth Elements (REEs) are correct?
1. REEs include all lanthanides along with Scandium and Yttrium.
2. China dominates global production and processing of Rare Earth Elements (REEs).
3. In India, Major deposits of rare earth elements are found in inland rocky regions.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: What are rare earths, why are they so vital?
Rare Earth Elements (REEs):
- REEs include 17 elements: 15 lanthanides + Scandium (Sc) + Yttrium (Y). Hence statement 1 is correct.
- They are not very rare, but rarely found in economically exploitable concentrations.
- Key properties: magnetic, luminescent, conductive, essential for modern technology.
- Major uses: EV & hybrid vehicles, wind turbines, smartphones, flat screens, semiconductors, defence equipment.
- China dominates global production and processing, creating strategic supply risks. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- In India, REE deposits are mainly in coastal beach sands (Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Andhra, Maharashtra, Gujarat). Hence statement 3 is incorrect.
- Ore minerals in India: Monazite (rich in light REEs), Bastnäsite (for medium REEs).
- India lacks significant heavy/critical REEs like Dysprosium, Terbium, Europium.
- Government initiative: National Critical Minerals Mission (2025) aims to secure supply and promote domestic processing.
- Strategic importance: REEs are vital for clean energy transition, high-tech manufacturing, and national security.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2025) Q. Consider the following statements: Statement I: Some rare earth elements are used in the manufacture of flat television screens and computer monitors. Statement II: Some rare earth elements have phosphorescent properties. Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements? (a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I (b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I (c) Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect (d) Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement II is correct |
9. The Kunming Biodiversity Fund (KBF) is:
(a) A bilateral fund by China and India for biodiversity projects
(b) A fund under the World Bank for climate finance
(c) A UN fund exclusively for marine biodiversity
(d) A multi-partner trust fund set up by China and UNEP
Answer: (d) A multi-partner trust fund set up by China and UNEP
Explanation:
In NEWS: Seven countries secure $5.8million from Kunming Biodiversity Fund to make agriculture more nature-friendly
Kunming Biodiversity Fund (KBF):
- KBF is a Multi-Partner Trust Fund (MPTF) set up by China and UNEP to support global biodiversity action. Hence option (d) is correct.
- Initial seed funding: ≈ US$200–230 million contributed by China.
- Launched formally in May 2024, announced at CBD COP15 in Kunming, China.
- Objective: To help developing countries implement the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KM-GBF) and their National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs).
- Focus areas: policy & law reform, capacity building, multilateral cooperation, and mobilizing financial resources.
- Works mainly through grant support to countries, emphasizing transparency and global cooperation.
- Governance: Executive Council (China, UNEP, SCBD), Interim Secretariat hosted at UNEP, and Independent Technical Advisory Group (ITAG).
- In 2025, approved 22 full-size projects in 34 countries and committed US$5.8 million for FAO-led biodiversity projects.
- Significance: Strengthens global biodiversity finance, supports sustainable development, and offers partnership opportunities for India.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2023) Q. Invasive Species Specialist Group’ (that develops Global Invasive Species Database) belongs to which one of the following organisations? (a) The International Union for Conservation of Nature (b) The United Nations Environment Programme (c) The United Nations World Commission for Environment and Development (d) The World Wide Fund for Nature |
10. According to the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, which of the following animals cannot be hunted by any person except under some provisions provided by law?
1. Gharial
2. Indian wild ass
3. Wild buffalo
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (d) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
Under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, animals under Schedule I cannot be hunted except under specific legal provisions.
- Gharial – Listed in Schedule I – Fully protected.
- Indian wild ass – Listed in Schedule I – Fully protected.
- Wild buffalo – Listed in Schedule I – Fully protected.
All three are critically endangered or endangered species under the Act and hunting is prohibited except under very special conditions permitted by law.

