1. Consider the following statements:
I. The inflation target in India is set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), in consultation with the Government of India.
II. The inflation target in India is based on core CPI inflation.
III. If the inflation remains outside the 2–6% band for three consecutive quarters, the RBI must submit a report to the Government
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) I and III
(d) III only
Answer: (d) III only
Explanation:
In NEWS: Inflation lessons: On the inflation data and the RBI
India’s Inflation Targeting Framework:
- Inflation targeting in India refers to the monetary policy framework where the central bank (RBI) aims to maintain inflation at a targeted level, using tools like interest rates.
- It was formally adopted in 2016 after the amendment of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 through the Finance Act, 2016.
- The amended RBI Act provides for a Monetary Policy Framework Agreement (MPFA) between the Government of India and the RBI.
- Under this framework, the primary objective of monetary policy is to maintain price stability, while keeping in mind the objective of growth.
The targeted inflation rate is:
- 4% Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation,
- With a tolerance band of ±2%, i.e., minimum 2% and maximum 6%.
- The inflation target in India is set by the Government of India, in consultation with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Henec statement I is incorrect.
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is responsible for setting the policy (repo) rate to meet this inflation target.
- The inflation target (4% ±2%) was first notified for the period 2016–2021, and later extended for 2021–2026.
- The inflation target in India is based on headline CPI inflation, not core inflation or WPI. Henec statement II is incorrect.
- If the inflation remains outside the 2–6% band for three consecutive quarters, the RBI must submit a report to the Government explaining:
- Reasons for failure
- Remedial actions
- Estimated time for returning to target. Hence statement III is correct.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2022) Q. In India, which one of the following is responsible for maintaining price stability by controlling inflation? (a) Department of Consumer Affairs (b) Expenditure Management Commission (c) Financial Stability and Development Council (d) Reserve Bank of India |
2. Which among the following are the areas of collaboration under the India-Australia Renewable Energy Partnership (REP)?
1. Solar and wind energy
2. Green hydrogen technology
3. Grid management and storage solutions
4. Clean energy investment and innovation
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Explanation:
In NEWS: Powering up the Australia-India clean energy partnership
India–Australia Renewable Energy Partnership (REP):
The India-Australia Renewable Energy Partnership (REP) was launched in September 2021 as part of both countries’ broader efforts to combat climate change and promote clean energy cooperation.
The partnership aims to advance renewable energy collaboration, especially in:
- Solar and wind energy
- Hydrogen technology (especially green hydrogen)
- Grid management and storage solutions
- Clean energy investment and innovation. Hence all are correct.
It supports the goals of:
- India’s National Hydrogen Mission
- Australia’s Technology Investment Roadmap
- The REP is aligned with both nations’ net-zero commitments — India by 2070 and Australia by 2050.
The partnership enhances:
- Public and private sector cooperation
- Research and development exchanges
- Policy dialogue and capacity building
- The REP also ties into the Indo-Pacific strategic cooperation, especially for promoting energy security and sustainable development in the region.
- It is part of the broader India–Australia Comprehensive Strategic Partnership, which includes trade, defense, education, and climate cooperation.
3. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) can assist disaster management authorities in which of the following ways?
1. Hazard zonation and vulnerability mapping
2. Evacuation route optimization
3. Real-time rainfall forecasting
4. Overlaying population density with flood zones
Select the correct answer using the code below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: (b) 1, 2 and 4 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: How to harness technology for effective disaster management
- Climate change has increased the frequency, intensity, and unpredictability of disasters such as floods, cyclones, cloudbursts, and landslides.
- Traditional disaster management approaches are reactive; there is now a need for proactive, data-driven systems using modern technology.
Role of Technology in Disaster Management:
A. Remote Sensing (RS)
- Provides real-time data through satellites, aircraft, or drones.
- Used for monitoring rainfall, land cover change, soil moisture, river flow, and detecting disaster-prone areas.
- Enables post-disaster assessment of damage and recovery.
B. Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
- Integrates spatial and non-spatial data for hazard mapping and risk analysis.
- Helps in evacuation route planning, vulnerability mapping, and decision support.
- Used in flood zonation, cyclone path tracking, and infrastructure planning.
Note: GIS is a spatial analysis tool; real-time rainfall forecasting depends on meteorological models, not GIS directly. Hence 3 is incorrect.
C. Sensor Networks / Internet of Things (IoT)
- Deployed in the field to provide real-time monitoring of rainfall, river levels, or soil moisture.
- Helps issue early warnings when thresholds are crossed.
- Improves accuracy of forecasting systems.
D. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) / Drones
- Used for rapid aerial surveys in inaccessible or high-risk zones.
- Helps in damage assessment, locating victims, and delivering relief materials.
- Provides high-resolution images to guide emergency response.
E. Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML)
- Processes large datasets for pattern recognition, prediction, and analysis.
- Used to forecast floods, landslides, and cyclones with higher accuracy.
- Helps optimize resource allocation and rescue operations.
F. Communication and Mobile Technologies
- Enable timely alerts to citizens via SMS, apps, or sirens.
- Ensure connectivity in disaster-hit areas through mesh and satellite networks.
- Facilitate real-time coordination among agencies.
G. Decision Support Systems (DSS)
- Integrate all data sources—RS, GIS, IoT, and AI—into interactive dashboards.
- Assist decision-makers with visualization, analytics, and scenario planning.
- Support multi-agency collaboration during disasters.
H. Geospatial Platforms
- Disseminate maps and real-time data to authorities and the public.
- Support transparency and preparedness planning.
- Example: National geoportals integrating hazard and vulnerability maps.
Indian Initiatives
- Sachet App – Real-time multilingual disaster alerts.
- Bhuvan Portal (ISRO) – Satellite-based disaster monitoring.
- Digital Panchanama (Maharashtra) – GPS-based damage assessment for quick compensation.
- Urban Flood Forecasting Systems – Localized flood prediction using sensors and GIS.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2015) Q. In which of the following activities are Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) satellites used? 1. Assessment of crop productivity 2. Locating groundwater resources 3. Mineral exploration 4. Telecommunications 5. Traffic studies Select the correct answer using the codes given below. (a) 1, 2 and 3 only (b) 4 and 5 only (c) 1 and 2 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 |
4. With reference to the Logistics Excellence, Advancement, and Performance Shield (LEAPS) 2025, consider the following statements:
1. It is a flagship initiative launched by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways as part of the Bharatmala project.
2. The initiative aims to benchmark and reward best practices in the logistics sector across India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (b) 2 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: Union Minister for Commerce and Industry, Shri Piyush Goyal launches LEAPS 2025 to benchmark logistics excellence in India
LEAPS 2025:
- LEAPS 2025 stands for Logistics Excellence, Advancement, and Performance Shield 2025.
- Launched by the Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- Implemented by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
- Announced during the 4th anniversary of PM GatiShakti at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi.
- The initiative aims to benchmark, recognise, and reward best practices in India’s logistics sector. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- Registrations opened in 2025, with a deadline of 15th November 2025.
Objectives
- To promote excellence, innovation, and sustainability in logistics operations.
- To encourage collaboration among industry, government, and academia.
- To enhance logistics efficiency and reduce costs across the supply chain.
- To strengthen India’s logistics ecosystem for a future-ready, globally competitive economy.
- To support national missions like Make in India, Atmanirbhar Bharat, and Viksit Bharat @ 2047.
Alignment with National Policies
- LEAPS 2025 aligns with the National Logistics Policy (NLP) 2022.
- It supports the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan for integrated infrastructure.
- The initiative contributes to India’s logistics cost reduction target and global competitiveness.
- It reinforces the government’s vision of “Whole-of-Government” approach in logistics reform.
Scope and Coverage
- Covers all major logistics modes: Air, Road, Rail, and Maritime freight operators.
- Includes Warehousing providers – industrial, consumable, and agricultural.
- Extends to Multimodal transport operators, MSMEs, and Startups.
- Involves Technology and operations service providers in logistics.
- Recognises Academic and Research institutions contributing to logistics education and innovation.
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetailm.aspx?PRID=2178621
5. Which one of the following statements best reflects the issue with the Durand Line, sometimes mentioned in the news?
(a) It is a disputed land corridor between India and China claimed by both countries in the Ladakh region.
(b) It is an old Silk Route boundary, now used as a trade corridor between Iran and Pakistan.
(c) It is the operational boundary between Afghanistan and Pakistan, whose legal status remains unrecognized by Afghanistan.
(d) It is a maritime boundary between Pakistan and the UAE, contested due to offshore energy resources.
Answer: (c) It is the operational boundary between Afghanistan and Pakistan, whose legal status remains unrecognized by Afghanistan.
Explanation:
In NEWS: Afghanistan and Pakistan face escalating border clashes. Deadly exchanges have erupted along the Durand Line, a border Afghanistan disputes.
Durand Line:
- The Durand Line is a 2,640-kilometre (1,640-mile) long international border between Afghanistan and Pakistan.
- Established in: 1893
Signed between:
- Sir Mortimer Durand (British diplomat, representing British India)
- Amir Abdur Rahman Khan (Emir of Afghanistan)
- Purpose: To demarcate the spheres of influence between British India and Afghanistan.
- The line runs through rugged, mountainous terrain, cutting across the Pashtun tribal areas and the Baloch region.
- It passes through provinces such as:
- Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (Pakistan)
- Balochistan (Pakistan)
- Eastern Afghanistan
Controversy and Disputes:
- Pakistan regards the Durand Line as its official international border with Afghanistan.
- Afghanistan has never officially accepted the Durand Line as an international border post-1947.
- Successive Afghan governments argue that the agreement was signed under duress.
- It divides ethnic Pashtuns and tribal communities, which Afghanistan considers a colonial imposition.
Hence option (c) is correct.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2022) Q. Which one of the following statements best reflects the issue with Senkaku Islands, sometimes mentioned in the news? (a) It is generally believed that they are artificial islands made by a country around South China Sea. (b) China and Japan engage in maritime disputes over these islands in East China Sea. (c) A permanent American military base has been set up there to help Taiwan to increase its defence capabilities. (d) Though International Court of Justice declared them as no man’s land, some South-East Asian countries claim them. |
6. Consider the following regions:
1. Paracel islands
2. Spratly islands
3. Senkaku islands
4. Pratas Islands
How many of the above regions are a part of the South China Sea?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
Answer: (c) Only three
Explanation:
In NEWS: Philippines, China trade blames for vessels colliding in South China Sea as tensions soar
- In the last few years, maritime East Asia has become an arena for intensified power politics. The East China Sea borders China, Taiwan, Japan, and South Korea.
- China asserts that the Senkaku/ Diaoyu islands, located in the East China Sea and under Japanese control, belong to Beijing. Hence 3 is incorrect.
- There have been multiple crises over these islands in the past. The South China Sea lies between China, Taiwan and five Southeast Asian countries — Vietnam, Malaysia, Brunei, the Philippines, and Indonesia — and has emerged as one of the most important flashpoints in the Indo-Pacific.
- China has been aggressively pushing its claims in the South China Sea.
- China views the East and South China Seas through the prism of sovereignty, territorial integrity, and national security. China’s Defence White paper, issued in 2019, declares, “South China Sea islands and Diaoyu Islands are inalienable parts of the Chinese territory.”
- In responding to the criticism regarding China’s activities, it asserts that “China exercises its national sovereignty to build infrastructure and deploy necessary defensive capabilities on the islands and reefs in the South China Sea, and to conduct patrols in the waters of Diaoyu Islands in the East China Sea.”
- What China perceives as its defensive actions are considered offensive and provocative by the regional countries surrounding theEast and South China Seas.
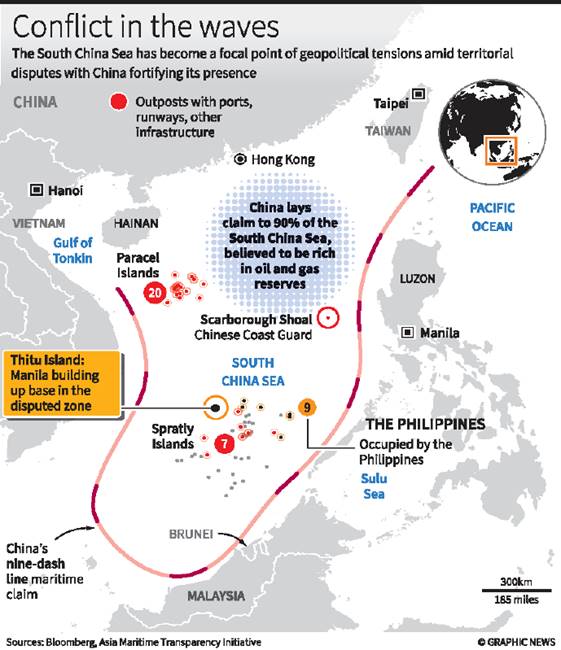
Hence option (c) is correct.
| PYQ REFERENCE: Q. Consider the following countries: 1. Finland 2. Germany 3. Norway 4. Russia How many of the above countries have a border with the North Sea? (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) Only three (d) All four |
7. With reference to the National Critical Mineral Stockpile (NCMS) in India, consider the following statements:
1. It is designed to ensure long-term availability of minerals critical to national security and economic growth.
2. The NCMS is designed to help India secure supply chains for minerals that are geopolitically sensitive and prone to supply disruptions
3. Domestically mined minerals are only eligible to be stored in the stockpile.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: The National Critical Mineral Stockpile (NCMS) is a forthcoming strategic initiative by the Government of India aimed at securing the nation’s supply of rare earth elements (REEs) and other critical minerals vital for emerging green technologies.
The National Critical Mineral Stockpile (NCMS):
- The National Critical Mineral Stockpile (NCMS) is a proposed initiative by the Government of India aimed at ensuring the strategic availability of critical minerals essential for the country’s economic and security interests. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The proposal was recommended in 2023 by the Ministry of Mines, under the Critical Minerals for India framework.
- The NCMS is designed to help India secure supply chains for minerals that are:
- Geopolitically sensitive
- Prone to supply disruptions Hence statement 2 is correct.
- Vital for sectors like renewable energy, electric vehicles, electronics, defense, and semiconductors
- Key critical minerals identified for stockpiling include:
- Lithium
- Cobalt
- Nickel
- Graphite
- Rare Earth Elements (REEs)
- Tungsten, among others.
- The stockpile would function as a strategic reserve, similar to the Strategic Petroleum Reserve (SPR) maintained for crude oil.
- It aims to:
- Reduce import dependency
- Improve national resilience
- Support India’s energy transition and Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) goals
- The KABIL initiative (Khanij Bidesh India Ltd), a joint venture of three public sector undertakings, plays a key role in acquiring strategic minerals from abroad. Hence statement 3 is incorrect.
- NCMS is aligned with India’s broader critical minerals strategy and is part of the vision to develop a critical minerals ecosystem domestically.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2025) Q. Consider the following statements: I. India has joined the Minerals Şecurity Partnership as a member. II. India is a resource-rich country in all the 30 critical minerals that it has identified. III. The Parliament in 2023 has amended the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 empowering the Central Government to exclusively auction mining lease and composite license for certain critical minerals. Which of the statements given above are correct? (a) I and II only (b) II and III only (c) I and III only (d) I, II and III |
Source: https://www.gktoday.in/national-critical-mineral-stockpile-ncms/
8. Consider the following statements with reference to the Kenton R. Miller Award:
I. It is conferred by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
II. The award recognizes individuals for innovation in the sustainable management of protected areas.
III. The award is presented annually during the UN Climate Change Conference (COP).
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I and II
(b) II only
(c) I and III
(d) III only
Answer: (b) II only
Explanation:
In NEWS: Kaziranga Director becomes first Indian to receive IUCN award for innovation in national parks
Kenton R. Miller Award:
- Dr. Sonali Ghosh, the Field Director of Kaziranga National Park and Tiger Reserve in Assam, has become the first Indian to receive the Kenton R. Miller Award presented by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- She received the award during the IUCN’s World Conservation Congress held in Abu Dhabi on 10 October 2025.
- The Kenton R. Miller Award is a prestigious international recognition granted by the World Commission on Protected Areas (WCPA) of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Hence statement I is incorrect.
- It honors individuals who have made exceptional innovations in the management and sustainability of protected areas such as national parks, wildlife reserves, and biosphere zones.
- The award is biennial (every two years), and it is typically presented during major IUCN conservation events, such as the World Conservation Congress. Hence statement III is incorrect.
Purpose of the Award:
This award highlights and encourages creative approaches in the conservation and sustainable use of protected areas. Hence statement II is correct.
It seeks to:
- Recognize pioneering leadership and visionary thinking
- Encourage innovation in:
- Protected area planning
- Governance and community engagement
- Monitoring and evaluation
- Sustainable financing
- Biodiversity protection
- Inspire others in the global conservation community to adopt and adapt innovative models
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2021) Q. Consider the following statements in respect of the Laureus World Sports Award which was instituted in the year 2000: 1. American golfer Tiger Woods was the first winner of this award. 2. The award was received mostly by ‘Formula One’ players so far. 3. Roger Federer received this award maximum number of times compared to others. Which of the above statements are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
9. Which of the following rivers meet(s) the Gomti River before it joins the Ganga?
1. Sai River
2. Varuna River
3. Kosi River
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: How UP govt plans to restore Gomti river to its ‘clean, uninterrupted, and pristine’ form
Gomti River:
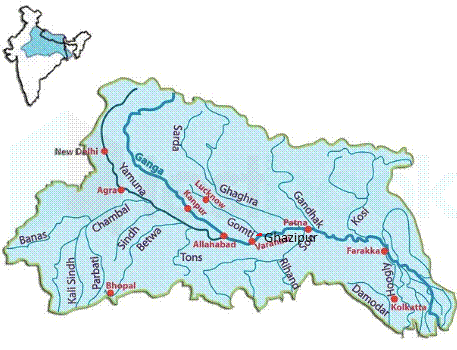
- The Gomti River is a tributary of the Ganga River.
- It flows entirely within Uttar Pradesh, making it an intra-state river.
- The river has a total length of about 940 kilometres.
Origin and Course
- The Gomti originates from Gomat Taal (Fulhaar Jheel) near Pipri village, Madhotanda, in Pilibhit district, Uttar Pradesh.
- It flows through major districts such as Pilibhit, Shahjahanpur, Sitapur, Lucknow, Sultanpur, and Jaunpur.
- The river finally joins the Ganga River near Saidpur, Kaithi, in Ghazipur district, Uttar Pradesh.
Tributaries
Major tributaries of the Gomti River include:
- Sai River
- Varuna River
- Kathina River
- Sarayan River
- Aril River
- Gaugauli River
- Bhainsi River
- Among these, the Sai River is a significant right-bank tributary. Hence 1 and 2 are correct.
Cities Located on its Banks
- Important cities situated along the Gomti River are:
- Lucknow (state capital)
- Sultanpur
- Jaunpur
- These cities depend heavily on the river for water supply, agriculture, and urban development.
Geographical Characteristics
- The Gomti flows through the middle Gangetic plain, characterized by alluvial fertile soil.
- It is seasonal in the upper reaches, with significant discharge during the monsoon season.
- The river supports agriculture in central and eastern Uttar Pradesh.
Environmental and Pollution Concerns
- The river faces severe pollution, especially in Lucknow, due to industrial effluents, sewage, and encroachment.
- Tannery and domestic waste are major contributors to water quality degradation.
- The Gomti Action Plan (GAP) was launched to restore and clean the river under the National River Conservation Plan (NRCP).
Projects and Initiatives
- Gomti Action Plan (GAP): Focused on cleaning and rejuvenating the river ecosystem.
- Gomti Riverfront Development Project: Aimed at river beautification and pollution control in Lucknow.
- Both initiatives fall under State and Central pollution control frameworks.
Cultural and Religious Significance
- The Gomti River is considered sacred in Hindu tradition.
- It is mentioned in ancient scriptures such as the Skanda Purana and Ramayana.
- Pilgrims perform rituals and holy dips along its banks, especially in Jaunpur and Sultanpur.
Economic Importance
- The river supports irrigation, agriculture, and fisheries in Uttar Pradesh.
- Provides drinking water to urban centres like Lucknow.
- Plays a role in groundwater recharge and floodplain agriculture.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2024) Q. With reference to the Himalayan rivers Joining the Ganga downstream of Prayagraj from West to East, which one of the following sequences is correct? (a) Ghaghara — Gomati — Gandak — Kosi (b) Gomati — Ghaghara — Gandak – Kosi (c) Ghaghara — Gomati — Kosi – Gandak (d) Gomati — Ghaghara — Kosi – Gandak |
10. In nature, which of the following is/are most likely to be found surviving on a surface without soil?
1. Fern
2. Lichen
3. Moss
4. Mushroom
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: (c) 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
- Ferns usually require moist, shaded environments with some soil or organic matter. They are not typically found on completely soil-less surfaces.
- Lichens are pioneer species that grow directly on bare rocks, bark, walls, etc. They are symbiotic associations of fungi and algae or cyanobacteria, and they do not require soil.
- Mosses can grow on rocks, tree bark, and moist surfaces, often without soil. They absorb water and nutrients directly from the air and rain.
- Mushrooms are fungi that grow on decaying organic matter, usually found in soil, wood, or other decomposing substrates. While they don’t need traditional soil, they require organic material, so they’re not commonly found on truly soil-less surfaces like bare rock.
Hence option (c) is correct.

