1. Consider the following statements:
- Makhana or Gorgon plant, is a species of water lily found in southern and eastern Asia.
- In India, Madhya Pradesh produces 90% of the world’s makhana.
- Makhana is approved under the One District One Product scheme
- Makhana contains a low amount of sodium and a high amount of potassium, which is good for cardiac health.
- The ideal conditions for cultivation of makhana includes a temperature range of 20°C to 35°C with relative humidity between 50% and 90% and annual rainfall of 100 to 250 cm.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(b) 2, 4 and 5
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 5
Answer: (a) 1, 3, 4 and 5
Explanation:
In NEWS: Prime Minister launched the National Makhana Board in Bihar.
Makhana (black diamond):
- Euryale ferox, commonly known as prickly water lily, makhana, or Gorgon plant, is a species of water lily found in southern and eastern Asia, and the only extant member of the genus Euryale. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The edible seeds, called fox nuts or makhana, are dried, and eaten predominantly in Asia.
- The plant is cultivated for its seeds in lowland ponds in India, China, and Japan.
- The Indian state of Bihar produces 90% of the world’s fox nuts. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
- The Chinese have cultivated the plant for centuries.
- In India, more than 96,000 hectares of Bihar were set aside for cultivation of Euryale in 1990–1991.
- In the northern and western parts of India, the seeds are often roasted or fried, which causes them to pop like popcorn. It has gained popularity as a ‘superfood’ for its rich nutritional properties — makhana is nutrient-dense, low-fat, and an ideal “healthy snack”
Climatic conditions:
- Temperature: 20°C to 35°C
- Relative humidity :50% to 90%
- Annual rainfall: 100 to 250 cm
- Soil: Smooth loamy soil. Hence statement 5 is correct.
- Makhana is a product approved under the One District One Product scheme, under which subsidies are provided to food processors for branding, marketing, and developing infrastructure. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Health Benefits:
- It has high fibre content, low glycemic index and phytochemical constituents.
- It contains an insignificant amount of fat and is rich in protein.
- It prevents high blood pressure and sugar.
- The high calcium content with nominal saturated fat of makhana strengthens bones and muscles.
- Makhana contains a low amount of sodium and a high amount of potassium, which is good for cardiac health. Hence statement 4 is correct.

| PYQ REFERENCE: Q. Consider the following statements: 1. Moringa (drumstick tree) is a leguminous evergreen tree. 2. The Tamarind tree is endemic to South Asia. 3. In India, most of the tamarind is collected as minor forest produce. 4. India exports tamarind and seeds of moringa. 5. Seeds of moringa and tamarind can be used in the production of biofuels. Which of the statements given above are correct? a) 1, 2, 4 and 5 b) 3, 4 and 5 c) 1, 3 and 4 d) 1, 2, 3 and 5 |
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2166835
2. Which among the following initiatives are part of the National Logistics Policy (NLP)?
- LEAPS initiative to promote innovation and green logistics.
- Sectoral Policy for Efficient Logistics (SPEL).
- Multimodal Logistics Parks (MMLPs).
- Make in India 2.0 campaign.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: (a) 1, 2 and 3 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: India Marks Three Years of National Logistics Policy: Transforming India’s Supply Chain Ecosystem
The National Logistics Policy (NLP):
- The National Logistics Policy (NLP) was launched on 17 September 2022 by the Prime Minister.
- It is implemented by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- The policy aims to reduce logistics costs to global benchmarks and improve India’s ranking in the Logistics Performance Index (LPI) to top 25 by 2030.
- NLP is aligned with the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan for integrated infrastructure and multimodal transport.
- The Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP) integrates 30+ digital systems and has enabled 160 crore+ digital transactions.
- The Logistics Data Bank provides real-time tracking of 75 million EXIM containers across 101 ICDs.
- The LEADS Index (Logistics Ease Across Different States) evaluates state-level logistics performance.
- The LEAPS initiative promotes innovation in logistics, including MSMEs, startups, academia, and encourages green logistics. Hence 1 is correct.
- Multimodal Logistics Parks (MMLPs) are being developed as hubs integrating transport, customs, and storage. Hence 3 is correct.
- Sectoral Policy for Efficient Logistics (SPEL) provides sector-specific frameworks for industries like coal, steel, cement, and food processing. Hence 2 is correct.
- NLP emphasizes skill development, with universities and institutes offering logistics courses in collaboration with GatiShakti Vishwavidyalaya.
- The policy promotes green logistics through tools like the Transportation Emissions Measurement Tool (TEMT) aligned with global standards.
- Many States and UTs have adopted State Logistics Policies and Action Plans under NLP.
- Key challenges remain in infrastructure gaps, regulatory harmonization, and digital literacy among small operators.
Note: Make in India 2.0 campaign is a separate flagship initiative, not part of NLP. Hence 4 is incorrect.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (UPSC CAPF AC 2024) Q. Which of the following statements with regard to National Logistics Policy (NLP) is NOT correct? (a) NLP was launched in 2022 (b) NLP would improve the competitiveness of Indian goods. (c) NLP would enhance economic growth and increase employment opportunities (d) NLP would provide an opportunity for deleveraging balance sheets and providing fiscal space for investment in new infrastructure assets |
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2167224
3. With reference to the Montreal Protocol, consider the following statements:
- It is a legally binding international treaty under the Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer.
- The Kigali Amendment to the Protocol deals with phasing out Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) which is the potential source for Ozone depletion.
- India has not yet ratified the Kigali Amendment.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
Answer: (a) Only one
Explanation:
In NEWS: MoEFCC celebrated 31st World Ozone Day to commemorate the signing of the Montreal Protocol
Montreal Protocol:
- Adoption: Signed on 16 September 1987; entered into force on 1 January 1989.
- Objective: To phase out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances (ODS) such as CFCs, halons, carbon tetrachloride, methyl chloroform, etc.
- Legal Status: A legally binding international treaty under the Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer (1985). Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Membership: Universal ratification — all 198 UN member states are parties (the first treaty in UN history to achieve this).
Amendments / Adjustments:
- London (1990) – tightened controls, added new ODS.
- Copenhagen (1992) – accelerated phase-out schedules.
- Montreal (1997) & Beijing (1999) – further ODS controls.
- Kigali Amendment (2016) – added Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) (though HFCs do not deplete ozone, they are potent greenhouse gases). Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
- Financial Mechanism: The Multilateral Fund (MLF) established in 1991 helps developing countries meet compliance costs.
India’s Role:
- India has been a party since 1992. Hence statement 3 is incorrect.
- Phased out production and consumption of several ODS as per timelines.
- Ratified the Kigali Amendment in 2021.
Achievements:
- Nearly 99% of ODS phased out globally.
- Ozone layer showing signs of recovery — expected to return to 1980 levels by 2066 over Antarctica.
- Also contributed to climate change mitigation, since ODS are also greenhouse gases.
- Importance: Considered the most successful environmental treaty ever, with universal participation and effective compliance mechanisms.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2015) Q. Which one of the following is associated with the issue of control and phasing out of the use of ozone-depleting substances? (a) Bretton Woods Conference (b) Montreal Protocol (c) Kyoto Protocol (d) Nagoya Protocol |
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2167243
4. Hydroponic weed, recently seen is news which is seized under “Operation WeedOut”, is:
(a) A synthetic narcotic produced using chemical compounds.
(b) A high-potency cannabis grown without soil, using nutrient-rich solutions.
(c) A hallucinogenic drug derived from opium poppy.
(d) A pharmaceutical sedative misused as a recreational drug.
Answer: (b) A high-potency cannabis grown without soil, using nutrient-rich solutions.
Explanation:
In NEWS: DRI continues crackdown on drug trafficking syndicates under “Operation Weed Out”
Operation Weed Out:
- Operation Weed Out is a pan-India anti-narcotics crackdown launched by the Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) to target and dismantle drug trafficking syndicates, specifically those smuggling hydroponic cannabis (weed) into India.
- Supports the Government of India’s “Nasha Mukt Bharat” (Drug-Free India) initiative.
- Reinforces India’s zero-tolerance policy against narco-terror and cross-border smuggling.
- Sends a strong message to international drug syndicates using Indian airports.
Objective:
- To identify, intercept, and eliminate illegal networks smuggling hydroponically grown cannabis (A high-grade cannabis grown using nutrient-rich water, often indoors) into India, primarily from Thailand and other Southeast Asian countries. Hence option (b) is correct.
Operational Focus:
- Hydroponic weed smuggling via airports and courier networks
- Intelligence-based targeting of syndicates
- Coordinated action across multiple Indian cities
- Arrest of carriers, receivers, and financiers
How the Operation Works:
- Intelligence Gathering: Surveillance and intel-sharing with foreign and domestic agencies.
- Passenger Profiling: Monitoring suspicious air passengers, often coming from Bangkok, Thailand.
- Baggage Scanning: Seizure of concealed cannabis in checked-in luggage.
- Follow-up Raids: Immediate action to arrest the receivers and trace the financing.
- Legal Action: Arrests under the NDPS Act, 1985.
Source: https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2167182
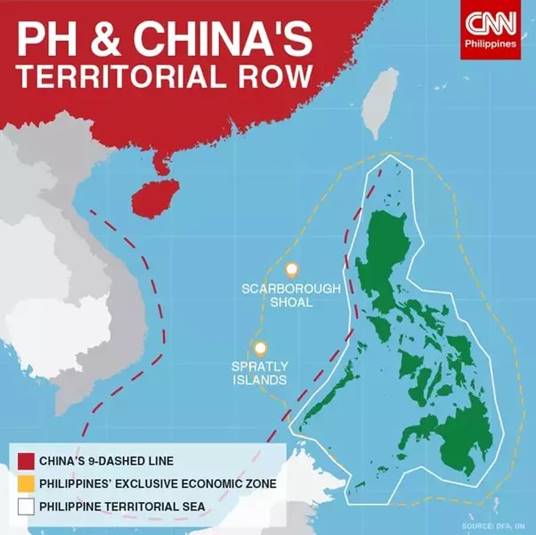
5. Which one of the following statements best reflects the issue with Scarborough Shoal, sometimes mentioned in the news?
(a) It is a coral atoll in the Indian Ocean claimed exclusively by India and Sri Lanka.
(b) It is a disputed maritime area in the South China Sea claimed by China, the Philippines, and Taiwan.
(c) A permanent American military base has been set up there to help Taiwan to increase its defence capabilities.
(d) It is an uninhabited island declared as a marine protected area by ASEAN countries with no territorial claims.
Answer: (b) It is a disputed maritime area in the South China Sea claimed by China, the Philippines, and Taiwan.
Explanation:
In NEWS: China says intercepted Philippine ships at disputed South China Sea shoal
Scarborough Shoal:
- Scarborough Shoal is a group of small islands and reefs located in the South China Sea, strategically positioned between the Philippines and China.
- It is claimed by multiple countries, primarily China, the Philippines, and Taiwan, leading to ongoing territorial disputes. Hence option (b) is correct.
- The area is rich in marine resources and lies near important shipping lanes, which makes it geopolitically significant.
- China asserts historical claims over almost the entire South China Sea, including Scarborough Shoal, based on the “Nine-Dash Line.”
- The Philippines contests this claim, citing proximity and international law, especially after the 2016 ruling by the Permanent Court of Arbitration that invalidated China’s expansive claims.
- Taiwan also claims sovereignty over the shoal, aligning largely with China’s claims.
- These overlapping claims have resulted in frequent confrontations, restrictions on fishing, and increased military presence in the area.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2022) Q. Which one of the following statements best reflects the issue with Senkaku Islands, sometimes mentioned in the news? (a) It is generally believed that they are artificial islands made by a country around South China Sea. (b) China and Japan engage in maritime disputes over these islands in East China Sea. (c) A permanent American military base has been set up there to help Taiwan to increase its defence capabilities. (d) Though International Court of Justice declared them as no man’s land, some South-East Asian countries claim them. |
6. Which one of the following best describes the concept of ‘Pink Tax’?
(a) A government-imposed tax on all products marketed towards women to promote gender equity.
(b) A luxury tax applied to imported cosmetics and personal care products regardless of gender.
(c) The extra amount women are often charged for certain products or services that are marketed specifically to them, despite being similar or identical to men’s versions.
(d) A discount provided on feminine hygiene products to reduce the financial burden on women.
Answer: (c) The extra amount women are often charged for certain products or services that are marketed specifically to them, despite being similar or identical to men’s versions.
Explanation:
In NEWS: Stop paying more for being a woman: avoid Pink Tax
Pink Tax:
- The Pink Tax is not an actual tax imposed by the government. Rather, it is a form of gender-based price discrimination where women are charged more than men for similar or identical products and services — simply because those items are marketed toward women. Hence option (c) is correct.
- The Pink Tax is a subtle, yet widespread form of market-driven gender inequality, where being a woman can cost more — not in taxes, but in everyday purchases.
- Awareness, comparison, and smarter choices can help avoid it, and contribute to economic fairness.
- Over a lifetime, women may spend thousands of rupees more on basic essentials than men.
- This financial burden is compounded by the gender wage gap and affects household savings, especially where women are not earning.
Examples:
- Haircuts: Women’s haircuts often cost more than men’s, even when the length and time taken are similar.
- Pink toys: Toys marketed to girls are often priced higher than similar toys for boys.
- Personal care: Products like razors, shampoos, deodorants, body lotions, and skincare are costlier for women — despite being functionally the same.
Pink Tax in India:
- Awareness is low: As per IFSA, 67% of Indians have never heard of the Pink Tax.
- A major step: In 2018, the Indian government removed GST on sanitary napkins and tampons, which previously had 12% tax — a small but important win against gender-based pricing.
- NCDRC Ruling: India’s top consumer forum ruled that fair pricing must be followed, discouraging gender-based price differences.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2016) Q. The term ‘Base Erosion and Profit Shifting’ is sometimes seen in the news in the context of (a) mining operation by multinational companies in resource-rich but backward areas (b) curbing of the tax evasion by multinational companies (c) exploitation of genetic resources of a country by multinational companies (d) lack of consideration of environmental planning and developmental costs in the implementation of projects |
7. With reference to India’s deep-sea mineral exploration, consider the following statements:
- India has the rights to explore polymetallic sulphides in the Carlsberg Ridge of the Indian Ocean.
- India can both explore and commercially mine the deep sea mineral resources in the Indian Ocean.
- The exploration activities are governed by the provisions of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (c) 1 and 3 only
Explanation:
In NEWS: India gets licence to scour new part of Indian Ocean for precious metals
India’s deep-sea mineral exploration:
- India has secured an exploration licence from the International Seabed Authority (ISA) to explore polymetallic sulphides in the Carlsberg Ridge region of the Indian Ocean. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The area allocated for exploration covers about 300,000 sq km.
- The minerals targeted include cobalt, copper, nickel, and manganese, which are critical for clean energy technologies.
- The licence is for exploration only, not commercial mining. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
- India already holds earlier ISA contracts:
- 2002: Polymetallic nodules in the Central Indian Ocean Basin.
- 2016 (valid till 2031): Polymetallic sulphides in parts of the Indian Ocean Ridge.
- The exploration is regulated under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and supervised by ISA. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- Environmental concerns exist regarding deep-sea exploration, including risks to biodiversity and fragile marine ecosystems.
- This move strengthens India’s access to critical minerals required for energy transition and enhances its strategic presence in the Indian Ocean.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2021) Q. Consider the following statements: 1. The Global Ocean Commission grants licences for seabed exploration and mining in international waters. 2. India has received licences for seabed mineral exploration in international waters 3. ‘Rare earth minerals’ are present on the seafloor in international waters. Which of the statements given above are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
8. Consider the following statements:
- A site or property must be on a country’s Tentative List before it can be nominated for inscription in the list of UNESCO Heritage Sites.
- The Tentative List has to be revised and updated by the countries every 10 years at least.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (c) Both 1 and 2
Explanation:
In NEWS: Andhra’s Tirumala Hills, Erra Matti Dibbalu eye World Heritage tag
UNESCO Tentative List:
- A Tentative List is an inventory of sites that a State Party (i.e. a country that has ratified the World Heritage Convention) may consider nominating in the future for inscription on the UNESCO World Heritage List.
- A site or property must be on a country’s Tentative List before it can be nominated for inscription. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The Tentative List is not exhaustive; it’s expected that countries revise them and update them every 10 years at least. Hence statement 2 is correct.
UNESCO Nomination Process – Key Steps:
1. Tentative List: A country first identifies potential heritage sites in a Tentative List — only these can be nominated.
2. Nomination Dossier: A detailed file is prepared, including maps, legal status, authenticity, comparative analysis, and management plans.
3.Review for Completeness: UNESCO checks if the dossier is complete. Incomplete ones are returned for revision.
4. Advisory Body Evaluation:
- ICOMOS evaluates cultural sites
- IUCN evaluates natural sites
- ICCROM provides conservation guidance (mainly for cultural sites)
5. Committee Decision: The World Heritage Committee reviews evaluations and decides to inscribe, defer, refuse, or request more info.
6. Selection Criteria: The site must show Outstanding Universal Value (OUV) and meet at least one of 10 criteria in the Operational Guidelines.
Selection criteria:
- to represent a masterpiece of human creative genius;
- to exhibit an important interchange of human values, over a span of time or within a cultural area of the world, on developments in architecture or technology, monumental arts, town-planning or landscape design;
- to bear a unique or at least exceptional testimony to a cultural tradition or to a civilization which is living or which has disappeared;
- to be an outstanding example of a type of building, architectural or technological ensemble or landscape which illustrates (a) significant stage(s) in human history;
- to be an outstanding example of a traditional human settlement, land-use, or sea-use which is representative of a culture (or cultures), or human interaction with the environment especially when it has become vulnerable under the impact of irreversible change;
- to be directly or tangibly associated with events or living traditions, with ideas, or with beliefs, with artistic and literary works of outstanding universal significance. (The Committee considers that this criterion should preferably be used in conjunction with other criteria);
- to contain superlative natural phenomena or areas of exceptional natural beauty and aesthetic importance;
- to be outstanding examples representing major stages of earth’s history, including the record of life, significant on-going geological processes in the development of landforms, or significant geomorphic or physiographic features;
- to be outstanding examples representing significant on-going ecological and biological processes in the evolution and development of terrestrial, fresh water, coastal and marine ecosystems and communities of plants and animals;
- to contain the most important and significant natural habitats for in-situ conservation of biological diversity, including those containing threatened species of outstanding universal value from the point of view of science or conservation.
| PYQ REFERENCE: (2024) Q. Which one of the following was the latest inclusion in the Intangible Cultural Heritage List of UNESCO? (a) Chhau dance (b) Durga puja (c) Garba dance (d) Kumbh mela |
https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/
9. Which one of the following is the correct description of the Gussadi Dance?
(a) A traditional tribal dance form wearing elaborate headgear made of peacock feathers performed by the Gond and Raj Gond communities, primarily in the Telangana region of India.
(b) A classical Indian dance from Odisha known for its graceful hand gestures and storytelling of Lord Krishna’s life, usually performed in temples and cultural festivals.
(c) A vibrant folk dance from Punjab characterized by energetic group movements and the use of sticks, performed to celebrate the harvest season and community unity.
(d) A masked ritual dance performed by Buddhist monks in the Himalayas, symbolizing the victory of good over evil, usually held during special religious ceremonies in monasteries.
Answer: (a) A traditional tribal dance form wearing elaborate headgear made of peacock feathers performed by the Gond and Raj Gond communities, primarily in the Telangana region of India.
Explanation:
In NEWS: Members of the Raj Gond tribe from Adilabad district of Telangana rehearsing Gussadi dance for the 78th Hyderabad Liberation Day celebrations.
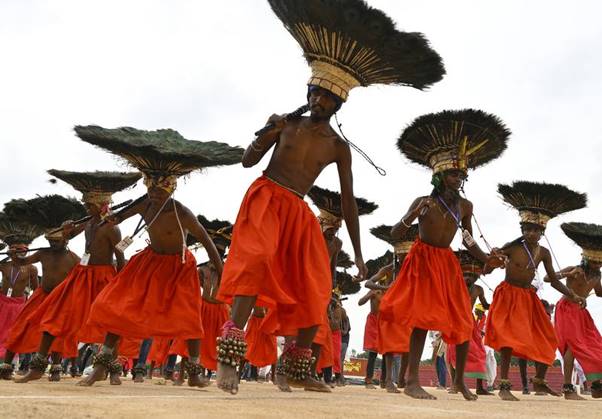

Gussadi Dance:
- Gussadi is a traditional tribal dance form performed by the Gond and Raj Gond communities, primarily in the Telangana region of India.
- It is mainly associated with the Dandari Festival, celebrated after Diwali, and is seen as a form of ancestral worship and thanksgiving.
- Gussadi dancers wear elaborate headgear made of peacock feathers, animal fur, and body paint, often taking days to prepare.
- The dance is traditionally performed by men, who move from village to village, dancing and enacting stories from tribal folklore and mythology.
- It is particularly popular in the Adilabad district of Telangana, especially among the Raj Gond tribes of Komaram Bheem Asifabad, Utnoor, and Narnoor regions.
- Gussadi is more than a dance—it’s a spiritual and cultural ritual, symbolizing harvest joy, cultural pride, and tribal identity.
- The performers are usually led by a “Pujari” (priest) who conducts rituals before and after the performance.
- The dance has been passed down orally and through practice, making it a vital part of the intangible cultural heritage of the region.
- Telangana government has taken steps to promote and preserve Gussadi as part of tribal cultural preservation.
- Komaram Bheem, a tribal freedom fighter and symbol of resistance, is often remembered in connection with Gussadi traditions.
Hence option (a) is correct.
| PYQ REFERENCE: Q. With reference to the famous Sattriya dance, consider the following statements: 1. Sattriya is a combination of music, dance and drama. 2. It is a centuries-old living tradition of Vaishnavites of Assam. 3. It is based on classical Ragas and Talas of devotional songs composed by Tulsidas, Kabir and Mirabai. Which of the statements above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Source: The Hindu
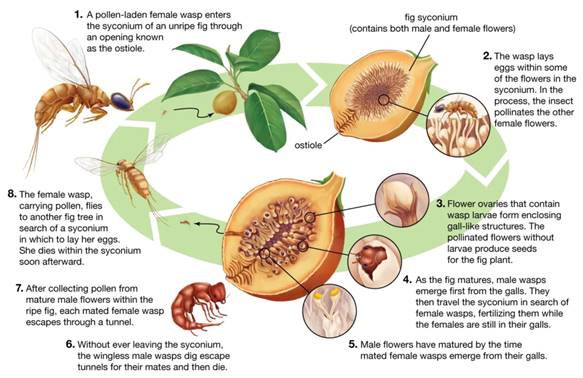
10. Which one of the following shows a unique relationship with an insect that has coevolved with it and that is the only insect that can pollinate this tree?
(a) Fig
(b) Mahua
(c) Sandalwood
(d) Silk cotton
Answer: (a) Fig
EXPLANATION: