News: 2023-24 El Nino among five strongest on record, will continue fueling heat in 2024: WMO
Q1. According to the WMO, the year 2023-24 El Niño is one of the five strongest on record and is gradually weakening, but it will continue to impact climate around the world. With respect to the aforementioned statement, explain the phenomena of El-Niño, La-Nina, ENSO and also how it affects the Indian Climate along with the Indian Ocean Dipole.
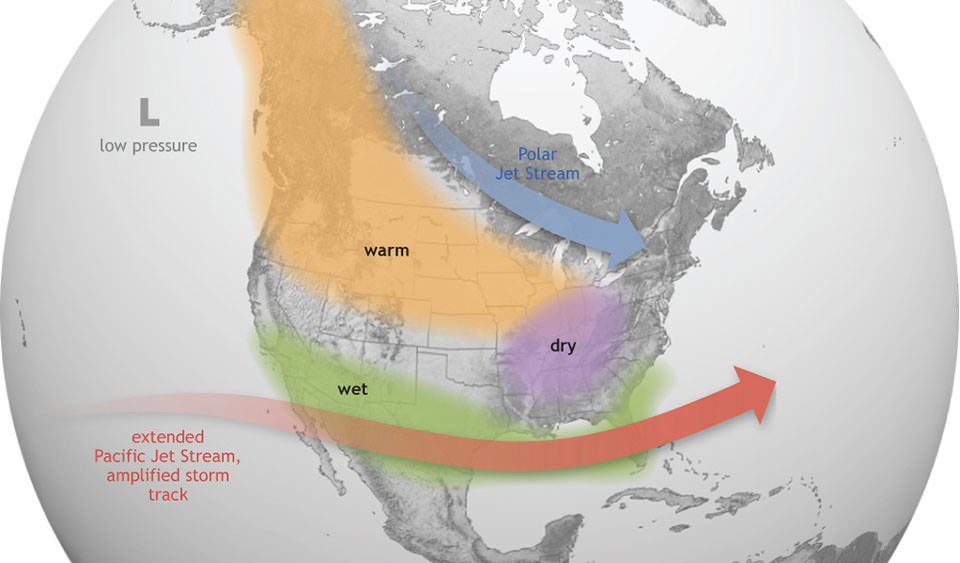
In a normal year, the eastern side of the Pacific Ocean, near the north-western coast of South America, is cooler than the western side near the islands of Philippines and Indonesia. This happens because the prevailing wind systems that move from east to west sweep the warmer surface waters towards the Indonesian coast.
The relatively cooler waters from below come up to replace the displaced water. An El Nino event is the result of a weakening of wind systems that leads to lesser displacement of warmer waters. This results in the eastern side of the Pacific becoming warmer than usual. During La Nina, the opposite happens.
About El-Niño:
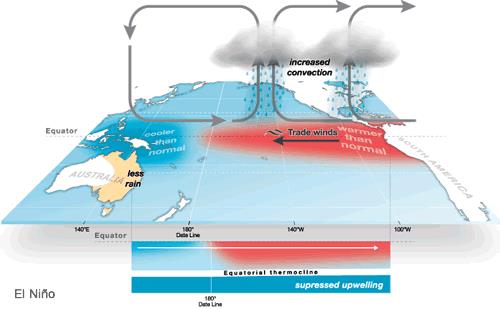
● El Niño refers to the abnormal warming of sea surface waters in the equatorial Pacific Ocean. El Niño episodes emerge naturally during autumn-summer in the northern hemisphere, typically once every 2-7 years.
● It peaks during winter (October-February) before weakening in the subsequent summer, making it a phenomenon that typically lasts for between 9 and 12 months. Occasionally, El Niño will last up to two years in a row.
About ENSO:
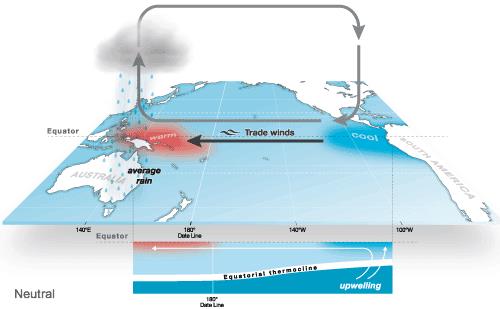
- ENSO (El Nino Southern Oscillation) refers to the oscillation between the El Nino and the La Nina. ENSO shifts irregularly back and forth between El Nino and La Niña every two to seven years. The Southern Oscillation part of the term ENSO refers to the atmospheric component: the shifting of atmospheric pressure between the central/eastern Pacific and the western Pacific.
About La-Nina:
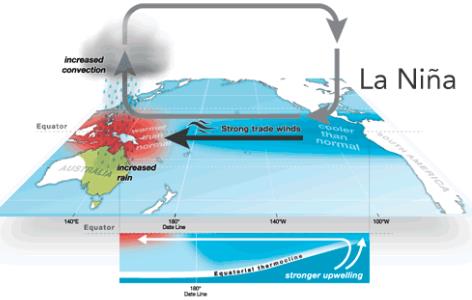
- La Niña occurs as an enhanced version of the neutral state. When air pressure is higher-than-average in Tahiti and lower-than-average in Australia, the easterly trade winds blow more intensely than usual.
- The colder-than-normal ocean water extends across the eastern and central equatorial Pacific, and the winds continue to push water westward, once again increasing the sea level around Indonesia. The water in the western Pacific warms up, which then increases precipitation in the region.
How does El-Nino affect the Indian Monsoon?
- The four-month southwest monsoon is India’s economic lifeline. The country receives nearly 70% of its annual rainfall (880 mm) during the June to September period. A good monsoon is crucial for sustaining the agrarian economy and for replenishment of the country’s water reservoirs.
- El Niño episodes affect the global weather, lead to an increase in temperatures and large-scale dryness and droughts, and disrupt normal rainfall patterns globally. Large parts of East Africa have experienced multiple failed rainy seasons in recent years, in part due to El Niño conditions.
- Over India, the El Nino has the impact of suppressing monsoon rainfall. The IOD is an ocean-atmosphere interaction very similar to the El Nino fluctuations in the Pacific Ocean, playing out, as the name shows, in the Indian Ocean.
- IOD is said to be positive when the western side of the Indian Ocean, near the Somali coast, becomes warmer than the eastern Indian Ocean. It is negative when the western Indian Ocean is cooler. El-Nino along with positive IOD gives drought situation to India and floods when IOD is negative.